Page 111 - v11i4
P. 111
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bioprinting for translational toxicology
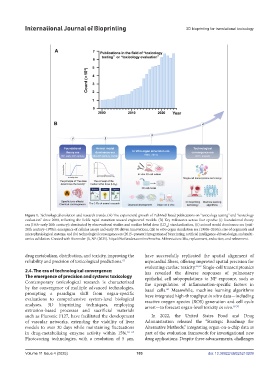
Figure 1. Technological evolution and research trends. (A) The exponential growth of PubMed-listed publications on “toxicology testing” and “toxicology
evaluation” since 2000, reflecting the field’s rapid transition toward engineered models. (B) Key milestones across four epochs: (i) foundational theory
era (16th–early 20th century): dominated by observational studies and median lethal dose (LD ) standardization, (ii) animal model dominance era (mid-
50
20th century–1970s): emergence of cellular assays and early 3R-driven innovations, (iii) in vitro organ simulation era (1980s–2010s): rise of organoids and
microphysiological systems, and (iv) technological convergence era (2015–present): integration of bioprinting, artificial intelligence-driven design, and multi-
omics validation. Created with Biorender [û, NP. (2025). https://BioRender.com/mu9mwhw. Abbreviation: 3Rs, replacement, reduction, and refinement.
drug metabolism, distribution, and toxicity, improving the have successfully replicated the spatial alignment of
reliability and precision of toxicological predictions. myocardial fibers, offering improved spatial precision for
62
evaluating cardiac toxicity. 66,67 Single-cell transcriptomics
2.4. The era of technological convergence: has revealed the diverse responses of pulmonary
The emergence of precision and systems toxicology epithelial cell subpopulations to NP exposure, such as
Contemporary toxicological research is characterized the upregulation of inflammation-specific factors in
by the convergence of multiple advanced technologies, basal cells. Meanwhile, machine learning algorithms
68
prompting a paradigm shift from organ-specific have integrated high-throughput in vitro data—including
evaluations to comprehensive system-level biological reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and cell cycle
analyses. 3D bioprinting techniques, employing arrest—to forecast organ-level toxicity in vivo. 69,70
extrusion-based processes and sacrificial materials
such as Pluronic F127, have facilitated the development In 2022, the United States Food and Drug
of vascular networks, extending the viability of liver Administration released the “Strategic Roadmap for
models to over 30 days while maintaining fluctuations Alternative Methods,” integrating organ-on-a-chip data as
in drug-metabolizing enzyme activity within 15%. 63–65 part of the evaluation framework for investigational new
Photocuring technologies, with a resolution of 5 μm, drug applications. Despite these advancements, challenges
Volume 11 Issue 4 (2025) 103 doi: 10.36922/IJB025210209