Page 166 - v11i4
P. 166
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-printed microstructure for bacteriostasis
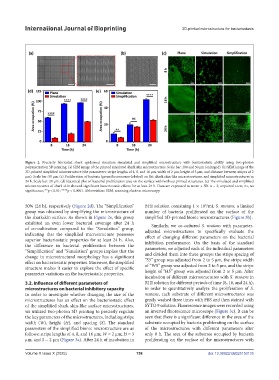
Figure 2. Precisely fabricated shark epidermal structure simulated and simplified microstructure with bacteriostatic ability using two-photon
polymerization 3D printing. (a) SEM image of the printed simulated shark skin microstructure. Scale bar: 200 and 50 μm (enlarged). (b) SEM image of the
3D-printed simplified microstructure (the parameters: stripe lengths of 4, 8, and 16 μm; width of 2 μm; height of 3 μm; and distance between stripes of 2
μm). Scale bar: 50 μm. (c) Proliferation of bacteria (green fluorescence-labeled) on flat, shark skin-like microstructures, and simplified microstructures in
24 h. Scale bar: 20 μm. (d) Statistical plot of bacterial proliferation area on the surface with/without printed structures. (e) The simulated and simplified
microstructures of shark skin showed significant bacteriostatic effects for at least 24 h. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. n = 3; unpaired t-test; ns, no
significance; **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001. Abbreviation: SEM, scanning electron microscopy.
50% (24 h), respectively (Figure 2d). The “Simplification” BHI solution containing 1 × 10 /mL S. mutans, a limited
6
group was obtained by simplifying the microstructure of number of bacteria proliferated on the surface of the
the sharkskin surface. As shown in Figure 2e, this group simplified 3D-printed bionic microstructures (Figure 3b).
exhibited an even lower bacterial coverage after 24 h Similarly, we co-cultured S. mutans with parameter-
of co-cultivation compared to the “Simulation” group, adjusted microstructures to specifically evaluate the
indicating that the simplified microstructure possesses effect of changing different parameters on the bacterial
superior bacteriostatic properties for at least 24 h. Also, inhibition performance. On the basis of the standard
the difference in bacterial proliferation between the parameters, we adjusted each of the individual parameters
“Simplification” and “Simulation” groups implies that the and divided them into three groups: the stripe spacing of
change in microstructural morphology has a significant “S5” group was adjusted from 2 to 5 μm, the stripe width
effect on bacteriostatic properties. Moreover, the simplified
structure makes it easier to explore the effect of specific of “W5” group was adjusted from 2 to 5 μm, and the stripe
parameter variations on the bacteriostatic properties. height of “H5” group was adjusted from 2 to 5 μm. After
incubation of different microstructures with S. mutans in
3.2. Influence of different parameters of BHI solution for different periods of time (8, 16, and 24 h),
microstructures on bacterial inhibitory capacity in order to quantitatively analyze the proliferation of S.
In order to investigate whether changing the size of the mutans, each substrate of different microstructures was
microstructures has an effect on the bacteriostatic effect gently washed three times with PBS and then stained with
of the simplified shark skin-like surface microstructures, SYTO 9 solution. Fluorescence images were recorded using
we utilized two-photon 3D printing to precisely regulate an inverted fluorescence microscope (Figure 3c). It can be
the key parameters of the microstructures, including stripe seen that there is a significant difference in the area of the
width (W), height (H), and spacing (S). The standard substrate occupied by bacteria proliferating on the surface
parameters of the simplified bionic microstructure are as of the microstructures with different parameters after
follows: stripe lengths of 4, 8, and 16 μm; W = 2 μm; H = 3 only 8 h. The area of the substrate occupied by bacteria
μm; and S = 2 μm (Figure 3a). After 24 h of incubation in proliferating on the surface of the microstructures with
Volume X Issue X (2025) 158 doi: 10.36922/IJB025150135