Page 182 - v11i4
P. 182
International Journal of Bioprinting Design of SLM-Ta artificial vertebral body
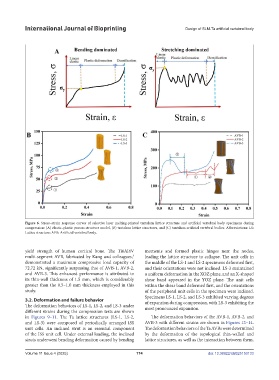
Figure 6. Stress–strain response curves of selective laser melting-printed tantalum lattice structure and artificial vertebral body specimens during
compression: (A) elastic–plastic porous structure model, (B) tantalum lattice structures, and (C) tantalum artificial vertebral bodies. Abbreviations: LS:
Lattice structure; AVB: Artificial vertebral body.
yield strength of human cortical bone. The Ti6Al4V moments and formed plastic hinges near the nodes,
multi-segment AVB, fabricated by Kang and colleagues, leading the lattice structure to collapse. The unit cells in
3
demonstrated a maximum compressive load capacity of the middle of the LS-1 and LS-2 specimens deformed first,
72.72 kN, significantly surpassing that of AVB-1, AVB-2, and their orientations were not inclined. LS-3 maintained
and AVB-3. This enhanced performance is attributed to a uniform deformation in the XOZ plane, and an X-shaped
its thin-wall thickness of 1.5 mm, which is considerably shear band appeared in the YOZ plane. The unit cells
greater than the 0.5–1.0 mm thickness employed in this within the shear band deformed first, and the orientations
study. of the peripheral unit cells in the specimen were inclined.
Specimens LS-1, LS-2, and LS-3 exhibited varying degrees
3.2. Deformation and failure behavior of expansion during compression, with LS-3 exhibiting the
The deformation behaviors of LS-1, LS-2, and LS-3 under most pronounced expansion.
different strains during the compression tests are shown
in Figures 9–11. The Ta lattice structures (LS-1, LS-2, The deformation behaviors of the AVB-1, AVB-2, and
and LS-3) were composed of periodically arranged ISS AVB-3 with different strains are shown in Figures 12–14.
unit cells. An inclined strut is an essential component The deformation behaviors of the Ta AVBs were determined
of the ISS unit cell. Under external loading, the inclined by the deformation of the topological thin-walled and
struts underwent bending deformation caused by bending lattice structures, as well as the interaction between them.
Volume 11 Issue 4 (2025) 174 doi: 10.36922/IJB025150133