Page 180 - v11i4
P. 180
International Journal of Bioprinting Design of SLM-Ta artificial vertebral body
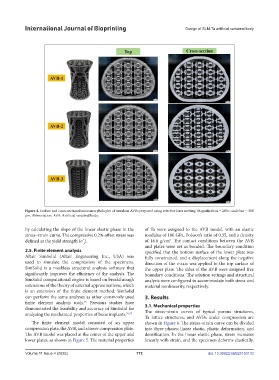
Figure 4. Surface and cross-sectional micromorphologies of tantalum AVBs prepared using selective laser melting. Magnification = 200×; scale bar = 300
μm. Abbreviation: AVB: Artificial vertebral body.
by calculating the slope of the linear elastic phase in the of Ta were assigned to the AVB model, with an elastic
stress–strain curve. The compressive 0.2% offset stress was modulus of 186 GPa, Poisson’s ratio of 0.35, and a density
defined as the yield strength (σ ). of 16.6 g/cm . The contact conditions between the AVB
*
3
y
and plates were set as bonded. The boundary condition
2.5. Finite element analysis specified that the bottom surface of the lower plate was
Altair SimSolid (Altair Engineering Inc., USA) was fully constrained, and a displacement along the negative
used to simulate the compression of the specimens. direction of the z-axis was applied to the top surface of
SimSolid is a meshless structural analysis software that the upper plate. The sides of the AVB were assigned free
significantly improves the efficiency of the analysis. The boundary conditions. The solution settings and structural
SimSolid computational engine is based on breakthrough analysis were configured to accommodate both stress and
extensions of the theory of external approximations, which material nonlinearity, respectively.
is an extension of the finite element method. SimSolid
can perform the same analyses as other commonly used 3. Results
55
finite element analysis tools. Previous studies have 3.1. Mechanical properties
demonstrated the feasibility and accuracy of SimSolid for The stress–strain curves of typical porous structures,
analyzing the mechanical properties of bone implants. 56,57
Ta lattice structures, and AVBs under compression are
The finite element model consisted of an upper shown in Figure 6. The stress–strain curve can be divided
compression plate, the AVB, and a lower compression plate. into three phases: linear elastic, plastic deformation, and
The AVB model was placed at the center of the upper and densification. In the linear elastic phase, stress increases
lower plates, as shown in Figure 5. The material properties linearly with strain, and the specimen deforms elastically.
Volume 11 Issue 4 (2025) 172 doi: 10.36922/IJB025150133