Page 463 - v11i4
P. 463
International Journal of Bioprinting Tunable GelMA-based bioinks for keloid modeling
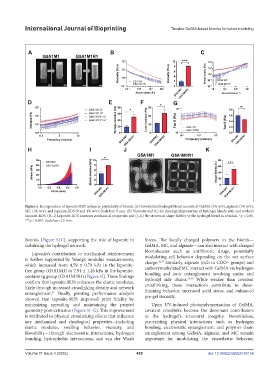
Figure 5. Incorporation of laponite-RDS enhances printability of bioink. (A) Crosslinked hydrogel blend consists of GelMA (5% w/v), alginate (1% w/v),
MC (1% w/v), and laponite-RDS (0 and 1% w/v). Scale bar: 5 mm. (B) Viscosity and (C–G) rheological properties of hydrogel blends with and without
laponite-RDS. (H–I) Laponite-RDS increases mechanical properties and (J–K) the structural shape fidelity of the hydrogel blend as a bioink. *p < 0.05,
***p < 0.001. Scale bar: 2.5 mm.
bioinks (Figure S1C), supporting the role of laponite in forces. The locally charged polymers in the bioink—
stabilizing the hydrogel network. GelMA, MC, and alginate—can also interact with charged
biomolecules such as antifibrotic drugs, potentially
Laponite’s contribution to mechanical reinforcement
is further supported by Young’s modulus measurements, modulating cell behavior depending on the net surface
38,39
which increased from 4.59 ± 0.79 kPa in the laponite- charge. Similarly, alginate (rich in COO– groups) and
carboxymethylated MC interact with GelMA via hydrogen
free group (G5A1M1) to 7.91 ± 1.26 kPa in the laponite- bonding and ionic entanglement involving amine and
containing group (G5A1M1R1) (Figure 5I). These findings hydroxyl side chains. 35,40 While weaker than covalent
confirm that laponite-RDS enhances the elastic modulus, crosslinking, these interactions contribute to shear-
likely through increased crosslinking density and network thinning behavior, increased yield stress, and enhanced
entanglement. Finally, printing performance analysis pre-gel viscosity.
37
showed that laponite-RDS improved print fidelity by
minimizing spreading and maintaining the printed Upon UV-induced photopolymerization of GelMA,
geometry post-extrusion (Figure 5J–K). This improvement covalent crosslinks become the dominant contributors
is attributed to physical crosslinking effects that influence to the hydrogel’s structural integrity. Nevertheless,
key mechanical and rheological properties—including pre-existing physical interactions such as hydrogen
elastic modulus, swelling behavior, viscosity, and bonding, electrostatic entanglement, and polymer chain
flowability—through electrostatic interactions, hydrogen entanglement among GelMA, alginate, and MC remain
bonding, hydrophobic interactions, and van der Waals important for modulating the viscoelastic behavior,
Volume 11 Issue 4 (2025) 455 doi: 10.36922/IJB025160154