Page 465 - v11i4
P. 465
International Journal of Bioprinting Tunable GelMA-based bioinks for keloid modeling
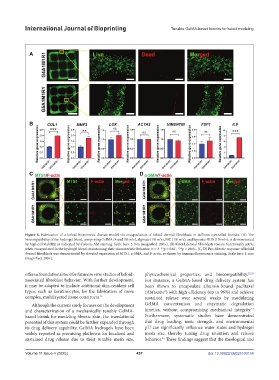
Figure 6. Fabrication of a keloid biomimetic disease model via encapsulation of keloid dermal fibroblasts in stiffness-controlled bioinks. (A) The
biocompatibility of the hydrogel blend, comprising GelMA (4 and 5% w/v), alginate (1% w/v), MC (1% w/v), and laponite-RDS (1% w/v), is demonstrated
by high cell viability, as indicated by Calcein-AM staining. Scale bars: 5 mm (magnified: 200×). (B) Keloid dermal fibroblasts remain functionally active
when encapsulated in the hydrogel blend, maintaining their characteristic behavior. n = 3. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (C, D) Pro-fibrotic response of keloid
dermal fibroblasts was demonstrated by elevated expression of MTS1, α-SMA, and F-actin, as shown by immunofluorescence staining. Scale bars: 1 mm
(magnified: 200×).
offers a foundational tool for future in vitro studies of keloid- physicochemical properties, and biocompatibility. 52,53
associated fibroblast behavior. With further development, For instance, a GelMA-based drug delivery system has
it may be adapted to include additional skin-resident cell been shown to encapsulate albumin-bound paclitaxel
types, such as keratinocytes, for the fabrication of more (Abraxane®) with high efficiency (up to 96%) and achieve
complex, multilayered tissue constructs. sustained release over several weeks by modulating
51
Although the current study focuses on the development GelMA concentration and enzymatic degradation
54
and characterization of a mechanically tunable GelMA- kinetics, without compromising mechanical integrity.
based bioink for modeling fibrotic skin, the translational Furthermore, systematic studies have demonstrated
potential of this system could be further expanded through that drug loading, ionic strength, and environmental
its drug delivery capability. GelMA hydrogels have been pH can significantly influence water states and hydrogel
widely reported as promising platforms for localized and mesh size, thereby tuning drug retention and release
sustained drug release due to their tunable mesh size, behavior. These findings suggest that the rheological and
26
Volume 11 Issue 4 (2025) 457 doi: 10.36922/IJB025160154