Page 37 - IJOCTA-15-1
P. 37
Global convergence property with inexact line search for a new conjugate gradient method
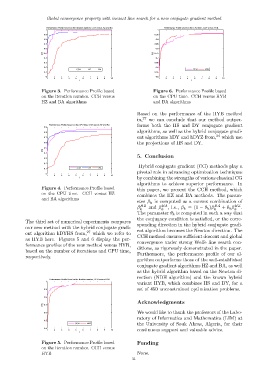
Performance Profile based on the iteration number, CCH versus HZ and BA. Performance Profile IJsed on the CPU time, CCH versus HYB.
1 1
0.9 0.95
0.8 0.9
0.7 0.85
0.6 0.8
P(f) 0.5 P(f) 0.75
0.4 0.7
0.3 0.65
0.2 0.6
CCH HZ BA CCH HYB
0.1 0.55
0 0.5
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
f f
Figure 3. Performance Profile based Figure 6. Performance Profile based
on the iteration number. CCH versus on the CPU time. CCH versus HYB
HZ and BA algorithms and BA algorithms
Based on the performance of the HYB method
in, 27 we can conclude that our method outper-
Performance Profile based on the CPU time, CCH versus HZ and BA. forms both the HS and DY conjugate gradient
0.9
algorithms, as well as the hybrid conjugate gradi-
0.8
ent algorithms hDY and hDYZ from, 34 which use
0.7
the projections of HS and DY.
0.6
0.5
P(f)
0.4
5. Conclusion
0.3
0.2
Hybrid conjugate gradient (CG) methods play a
CCH HZ BA
0.1
pivotal role in advancing optimization techniques
0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
f by combining the strengths of various classical CG
algorithms to achieve superior performance. In
Figure 4. Performance Profile based this paper, we present the CCH method, which
on the CPU time. CCH versus HZ
combines the HZ and BA methods. The param-
and BA algorithms
eter β k is computed as a convex combination of
β HZ and β BA , i.e., β k = (1 − θ k )β BA + θ k β HZ .
k k k k
The parameter θ k is computed in such a way that
the conjugacy condition is satisfied, or the corre-
The third set of numerical experiments compares
sponding direction in the hybrid conjugate gradi-
our new method with the hybrid conjugate gradi- ent algorithm becomes the Newton direction. The
ent algorithm hDYHS from, 27 which we refer to
CCH method ensures sufficient descent and global
as HYB here. Figures 5 and 6 display the per-
convergence under strong Wolfe line search con-
formance profiles of the new method versus HYB,
ditions, as rigorously demonstrated in the paper.
based on the number of iterations and CPU time, Furthermore, the performance profile of our al-
respectively.
gorithm outperforms those of the well-established
conjugate gradient algorithms HZ and BA, as well
as the hybrid algorithm based on the Newton di-
rection (NDH algorithm) and the known hybrid
Performance Profile IJsed on the iteration number, CCH versus HYB.
1
variant HYB, which combines HS and DY, for a
set of 450 unconstrained optimization problems.
0.9
0.8
Acknowledgments
P(f) 0.7
We would like to thank the professors of the Labo-
0.6
ratory of Informatics and Mathematics (LIM) at
0.5
CCH HYB the University of Souk Ahras, Algeria, for their
0.4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 continuous support and valuable advice.
f
Figure 5. Performance Profile based Funding
on the iteration number. CCH versus
HYB None.
31