Page 50 - IJOCTA-15-3
P. 50
M. Aychluh et.al. / IJOCTA, Vol.15, No.3, pp.407-425 (2025)
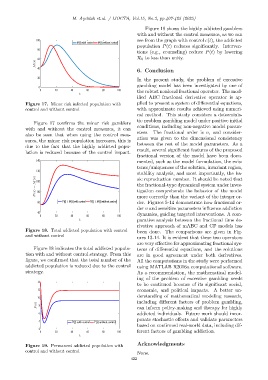
Figure 19 shows the highly addicted gamblers
with and without the control measures, as we can
100 see from the graph with control c(t), the addicted
M(t) with control M(t) without control
population P(t) reduces significantly. Interven-
80
tions (e.g., counseling) reduce P(t) by lowering
R 0 to less than unity.
60
M (t)
40
6. Conclusion
20
In the present study, the problem of excessive
gambling model has been investigated by one of
0
0 20 40 60 80 100 the robust nonlocal fractional operator. The mod-
t
ified ABC fractional derivative operator is ap-
Figure 17. Minor risk infected population with plied to present a system of differential equations,
control and without control with approximate results achieved using numeri-
cal method. This study considers a determinis-
tic problem gambling model under positive initial
Figure 17 confirms the minor risk gamblers
conditions, including non-negative model param-
with and without the control measures, it can
eters. The fractional order is υ, and consider-
also be seen that when using the control mea-
ation was given to the dimensional consistency
sures, the minor risk population increases, this is
between the rest of the model parameters. As a
due to the fact that the highly addicted popu-
result, several significant features of the proposed
lation is reduced because of the control impact.
fractional version of the model have been docu-
140 mented, such as the model formulation, the exis-
tence/uniqueness of the solution, invariant region,
120
stability analysis, and most importantly, the ba-
P (t) + M (t) 100 the fractional-type dynamical system under inves-
sic reproduction number. It should be noted that
tigation comprehends the behavior of the model
80
der. Figures 5-14 demonstrate how fractional or-
60 P(t)+M(t) with control P(t)+M(t) without control more correctly than the variant of the integer or-
der υ and sensitive parameters influence addiction
40
0 20 40 60 80 100 dynamics, guiding targeted interventions. A com-
t parative analysis between the fractional time de-
rivative approach of mABC and CF models has
Figure 18. Total addicted population with control been done. The comparisons are given in Fig-
and without control
ures 13-14. It is evident that these two operators
are very effective for approximating fractional sys-
Figure 18 indicates the total addicted popula- tems of differential equations, and the solutions
tion with and without control strategy. From this are in good agreement under both derivatives.
figure, we confirmed that the total number of the All the computations in the study were performed
addicted population is reduced due to the control using MATLAB R2016a computational software.
strategy. As a recommendation, the mathematical model-
ing of the problem of excessive gambling needs
14
to be continued because of its significant social,
12 economic, and political impacts. A better un-
derstanding of mathematical modeling research,
10
P (t) 8 including different factors of problem gambling,
can inform policy-making and therapy for highly
6 addicted individuals. Future work should incor-
porate stochastic effects and validate parameters
4 P(t) with control P(t) without control
based on confirmed real-world data, including dif-
2
0 20 40 60 80 100 ferent factors of gambling addiction.
t
Acknowledgments
Figure 19. Permanent addicted population with
control and without control
None.
422