Page 29 - IJOCTA-15-4
P. 29
Control strategies and power converter topologies for switched reluctance motors in electric...
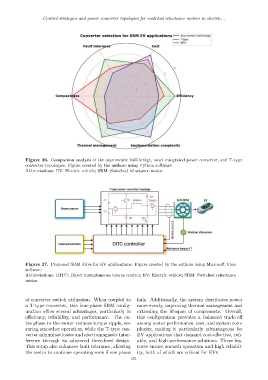
Figure 26. Comparison analysis of the asymmetric half-bridge, novel integrated power converter, and T-type
converter topologies. Figure created by the authors using Python software
Abbreviations: EV: Electric vehicle; SRM: Switched reluctance motor.
Figure 27. Proposed SRM drive for EV applications. Figure created by the authors using Microsoft Visio
software
Abbreviations: DITC: Direct instantaneous torque control; EV: Electric vehicle; SRM: Switched reluctance
motor.
of converter switch utilization. When coupled to fails. Additionally, the system distributes power
a T-type converter, this four-phase SRM config- more evenly, improving thermal management and
uration offers several advantages, particularly in extending the lifespan of components. Overall,
efficiency, reliability, and performance. The ex- this configuration provides a balanced trade-off
tra phase in the motor reduces torque ripple, en- among motor performance, cost, and system com-
suring smoother operation, while the T-type con- plexity, making it particularly advantageous for
verter minimizes losses and electromagnetic inter- EV applications that demand cost-effective, reli-
ference through its advanced three-level design. able, and high-performance solutions. These fea-
This setup also enhances fault tolerance, allowing tures ensure smooth operation and high reliabil-
the motor to continue operating even if one phase ity, both of which are critical for EVs.
571