Page 112 - IJPS-11-5
P. 112
International Journal of
Population Studies Endowment insurance and family consumption in China
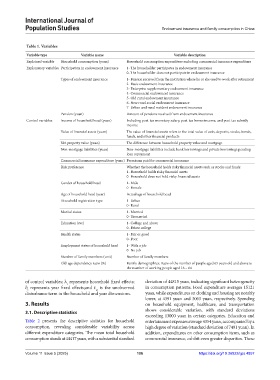
Table 1. Variables
Variable type Variable name Variable description
Explained variable Household consumption (yuan) Household consumption expenditure excluding commercial insurance expenditure
Explanatory variables Participation in endowment insurance 1- The householder participates in endowment insurance
0- The householder does not participate in endowment insurance
Types of endowment insurance 1- Pension received from the institution where he or she used to work after retirement
2- Basic endowment insurance
3- Enterprise supplementary endowment insurance
4- Commercial endowment insurance
5- Old rural endowment insurance
6- New rural social endowment insurance
7- Urban and rural resident endowment insurance
Pension (yuan) Amount of pensions received from endowment insurance
Control variables Income of household head (yuan) Including post-tax monetary salary, post-tax bonus income, and post-tax subsidy
income
Value of financial assets (yuan) The value of financial assets refers to the total value of cash, deposits, stocks, bonds,
funds, and other financial products
Net property value (yuan) The difference between household property value and mortgage
Non-mortgage liabilities (yuan) Non-mortgage liabilities include bank borrowings and private borrowings pending
loan repayment
Commercial insurance expenditure (yuan) Premiums paid for commercial insurance
Risk preference Whether the household holds risky financial assets such as stocks and funds:
1- Household holds risky financial assets
0- Household does not hold risky financial assets
Gender of household head 1- Male
0- Female
Age of household head (year) Actual age of household head
Household registration type 1- Urban
0- Rural
Marital status 1- Married
0- Unmarried
Education level 1- College and above
0- Below college
Health status 1- Fair or good
0- Poor
Employment status of household head 1- With a job
0- No job
Number of family members (unit) Number of family members
Old-age dependency ratio (%) Family demographics: Ratio of the number of people aged 65 years old and above to
the number of working people aged 16 – 64
of control variables; λ represents household fixed effects; deviation of 44815 yuan, indicating significant heterogeneity
t
δ represents year fixed effects;and ε is the unobserved in consumption patterns. Food expenditure averages 15121
i,t
t
disturbance term in the household and year dimensions. yuan, while expenditures on clothing and housing are notably
lower, at 4391 yuan and 3063 yuan, respectively. Spending
3. Results on household equipment, healthcare, and transportation
3.1. Descriptive statistics shows considerable variation, with standard deviations
exceeding 13000 yuan in certain categories. Education and
Table 2 presents the descriptive statistics for household entertainment expenses average 4354 yuan, accompanied by a
consumption, revealing considerable variability across high degree of variation (standard deviation of 7491 yuan). In
different expenditure categories. The mean total household addition, expenditures on other consumption items, such as
consumption stands at 44417 yuan, with a substantial standard commercial insurance, exhibit even greater disparities. These
Volume 11 Issue 5 (2025) 106 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.4857