Page 115 - IJPS-11-5
P. 115
International Journal of
Population Studies Endowment insurance and family consumption in China
implies that households with endowment insurance not
only display distinct consumption patterns compared to
those without coverage, but the actual pension income Join 175.47 (p=0.000) 0.16
further influences consumption decisions. (8) Other 1.01*** −0.03*** 2.27*** Yes Yes 1.68 (p=0.000) 35872
3.3. Impact of endowment insurance on household
consumption structure
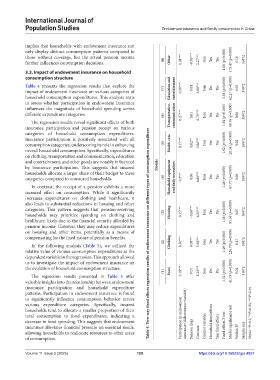
Table 4 presents the regression results that explore the Education and 0.01 Join Yes Yes 3.38 (p=0.000) 62.27 (p=0.000) 0.05 35872
impact of endowment insurance on various categories of (7) entertainment 0.36*** 3.88***
household consumption expenditures. This analysis aims
to assess whether participation in endowment insurance
influences the magnitude of household spending across
different expenditure categories. (6) Transportation communication 0.27*** 0.01 6.79*** Join Yes Yes 1.92 (p=0.000) 69.76 (p=0.000) 0.06 35872
The regression results reveal significant effects of both
insurance participation and pension receipt on various
categories of household consumption expenditures.
Insurance participation is positively associated with all
consumption categories, underscoring its role in enhancing (5) Health care 0.15*** 0.02** 5.66*** Join Yes Yes 1.92 (p=0.000) 28.54 (p=0.000) 0.02 35872
overall household consumption. Specifically, expenditures
on clothing, transportation and communication, education
and entertainment, and other goods are notably influenced
by insurance participation. This suggests that insured Models
households allocate a larger share of their budget to these
categories compared to uninsured households. (4) Household equipment and daily necessities 0.3*** 0.00 6.60*** Join Yes Yes 1.48 (p=0.000) 67.77 (p=0.000) 0.06 35872
In contrast, the receipt of a pension exhibits a more
nuanced effect on consumption. While it significantly
increases expenditures on clothing and healthcare, it
also leads to substantial reductions in housing and other
categories. This pattern suggests that pension-receiving
households may prioritize spending on clothing and (3) Housing 0.15*** −0.06*** 6.55*** Join Yes Yes 1.38 (p=0.000) 81.56 (p=0.000) 0.07 35872
healthcare, likely due to the financial security afforded by
pension income. However, they may reduce expenditures
on housing and other items, potentially as a means of Table 4. Two‑way fixed effects regression results of endowment insurance on different types of consumption expenditure
compensating for the fixed nature of pension benefits.
(2) Clothing 0.50*** 0.08*** 5.92*** Join Yes Yes 1.49 (p=0.000) 226.70 (p=0.000) 0.17 35872
In the following analysis (Table 5), we utilized the
relative value of various consumption expenditures as the
dependent variable in the regression. This approach allowed
us to investigate the impact of endowment insurance on
the evolution of household consumption structure.
(1) Food 0.18*** 0.01 8.23*** Join Yes Yes 1.52 (p=0.000) 41.79 (p=0.000) 0.04 35872
The regression results presented in Table 5 offer
valuable insights into the relationship between endowment
insurance participation and household expenditure
patterns. Participation in endowment insurance is found
to significantly influence consumption behavior across
various expenditure categories. Specifically, insured
households tend to allocate a smaller proportion of their Notes: *P<0.1; **P<0.05; ***P<0.01.
total consumption to food expenditures, indicating a Participation in endowment insurance (dichotomous variable)
decrease in food spending. This suggests that endowment Household fixed effects Model significance test
insurance alleviates financial pressure on essential needs, Pension (log) Control variables Year fixed effects Fixed effects F test
allowing households to reallocate resources to other areas Constant Within R² Sample size
of consumption.
Volume 11 Issue 5 (2025) 109 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.4857