Page 116 - IJPS-11-5
P. 116
International Journal of
Population Studies Endowment insurance and family consumption in China
Conversely, participation in endowment insurance
is positively associated with increased expenditures on
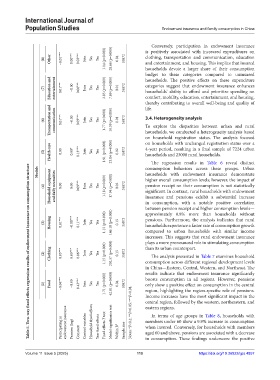
(8) Other −0.01*** 0.00*** 0.03*** Join Yes Yes 1.14 (p=0.000) 28.66 (p=0.000) 0.04 35872 clothing, transportation and communication, education
and entertainment, and housing. This implies that insured
households devote a larger share of their consumption
budget to these categories compared to uninsured
households. The positive effects on these expenditure
(7) Education and entertainment 0.01*** −0.00 0.06*** Join Yes Yes 2.85 (p=0.000) 7.89 (p=0.000) 0.01 35872 categories suggest that endowment insurance enhances
households’ ability to afford and prioritize spending on
comfort, mobility, education, entertainment, and housing,
thereby contributing to overall well-being and quality of
life.
(6) Transportation and communication 0.01*** −0.00 0.09*** Join Yes Yes 1.77 (p=0.000) 10.59 (p=0.000) 0.01 35872 3.4. Heterogeneity analysis
To explore the disparities between urban and rural
households, we conducted a heterogeneity analysis based
on household registration status. The analysis focused
on households with unchanged registration status over a
(5) Health care 0.00 0.00* 0.13*** Join Yes Yes 1.91 (p=0.000) 23.04 (p=0.000) 0.02 35872 4-year period, resulting in a final sample of 7224 urban
households and 23008 rural households.
The regression results in Table 6 reveal distinct
Table 5. Two‑way fixed effects regression results of endowment insurance on consumption structure
Models consumption behaviors across these groups. Urban
Household equipment 0.00 0.00 0.09*** Join Yes Yes 1.18 (p=0.000) 17.94 (p=0.000) 0.02 35872 higher overall consumption levels; however, the impact of
households with endowment insurance demonstrate
pension receipt on their consumption is not statistically
(4) and daily necessities significant. In contrast, rural households with endowment
insurance and pensions exhibit a substantial increase
in consumption, with a notable positive correlation
between pension receipt and higher consumption levels—
approximately 0.8% more than households without
(3) Housing 0.01*** −0.00*** 0.11*** Join Yes Yes 1.15 (p=0.000) 146.18 (p=0.000) 0.15 35872 pensions. Furthermore, the analysis indicates that rural
households experience a faster rate of consumption growth
compared to urban households with similar income
increases. This suggests that rural endowment insurance
plays a more pronounced role in stimulating consumption
(2) Clothing 0.03*** 0.00*** 0.06*** Join Yes Yes 1.15 (p=0.000) 202.57 (p=0.000) 0.15 35872 than its urban counterpart.
The analysis presented in Table 7 examines household
consumption across different regional development levels
in China—Eastern, Central, Western, and Northeast. The
results indicate that endowment insurance significantly
(1) Food −0.04*** −0.00 0.43*** Join Yes Yes 1.71 (p=0.000) 42.81 (p=0.000) 0.04 35872 boosts consumption in all regions. However, pensions
only show a positive effect on consumption in the central
region, highlighting the region-specific role of pensions.
Income increases have the most significant impact in the
central region, followed by the western, northeastern, and
In terms of age groups in Table 8, households with
Participating in endowment insurance Pension (log) Constant Control variables Household fixed effects Year fixed effects Fixed effects F test Model significance test Within R² Sample size Notes: *P<0.1; **P<0.05; ***P<0.01. eastern regions.
members under 60 show a 9.9% increase in consumption
when insured. Conversely, for households with members
aged 60 and above, pensions are associated with a decrease
in consumption. These findings underscore the positive
Volume 11 Issue 5 (2025) 110 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.4857