Page 12 - IJPS-9-1
P. 12
International Journal of
Population Studies Local population changes as a spatial varying multiscale process
2
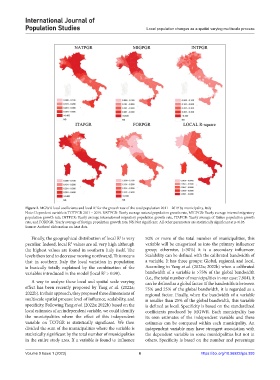
Figure 2. MGWR local coefficients and local R for the growth rate of the total population 2011 – 2019 by municipality, Italy
Note: Dependent variable is TOTPGR 2011 – 2019. NATPGR: Yearly average natural population growth rate, MIGPGR: Yearly average internal migratory
population growth rate, INTPGR: Yearly average international migratory population growth rate, ITAPGR: Yearly average of Italian population growth
rate, and FORPGR: Yearly average of foreign population growth rate, NS: Not significant. All other parameters are statistically significant at p<0.05.
Source: Authors’ elaboration on Istat data.
Finally, the geographical distribution of local R is very 50% or more of the total number of municipalities, this
2
peculiar. Indeed, local R values are all very high although variable will be categorized as into the primary influencer
2
the highest values are found in southern Italy itself. The group; otherwise, (<50%) it is a secondary influencer.
levels then tend to decrease moving northward. This means Scalability can be defined with the calibrated bandwidth of
that in southern Italy the local variation in population a variable. It has three groups: Global, regional, and local.
is basically totally explained by the combination of the According to Yang et al. (2022a; 2022b) when a calibrated
variables introduced in the model (local R > 0.98). bandwidth of a variable is >75% of the global bandwidth
2
(i.e., the total number of municipalities in our case: 7,904), it
A way to analyze these local and spatial scale varying can be defined as a global factor. If the bandwidth is between
effect has been recently proposed by Yang et al. (2022a; 75% and 25% of the global bandwidth, it is regarded as a
2022b). In their approach, they proposed three dimensions of regional factor. Finally, when the bandwidth of a variable
multiscale spatial process: level of influence, scalability, and is smaller than 25% of the global bandwidth, this variable
specificity. Following Yang et al. (2022a; 2022b) based on the is defined as local. Specificity is based on the standardized
local estimates of an independent variable, we could identify coefficients produced by MGWR. Each municipality has
the municipalities where the effect of this independent its own estimates of the independent variable and these
variable on TOTGR is statistically significant. We then estimates can be compared within each municipality. An
divided the sum of the municipalities where the variable is independent variable may have strongest association with
statistically significant by the total number of municipalities the dependent variable in some municipalities but not in
in the entire study area. If a variable is found to influence others. Specificity is based on the number and percentage
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.393