Page 82 - IJPS-9-1
P. 82
International Journal of
Population Studies COVID-19, economic crisis, insomnia, and stress
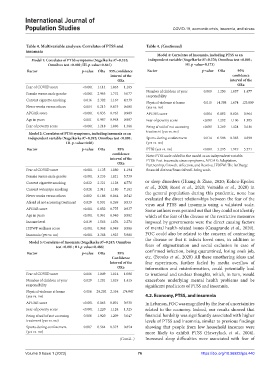
Table 4. Multivariable analyses: Correlates of PTSS and Table 4. (Continued)
insomnia
Model 4: Correlates of Insomnia, including PTSS as an
Model 1: Correlates of PTSS symptoms (Nagelkerke R =0.332; independent variable (Nagelkerke R =0.276; Omnibus test <0.001;
2
2
Omnibus test <0.001; HL p-value=0.845) HL p-value=0.173)
Factor p‑value ORa 95% confidence Factor p‑value ORa 95%
interval of the confidence
ORa interval of the
ORa
Fear of COVID score <0.001 1.114 1.065 1.165
Female versus male gender <0.001 2.965 1.732 5.077 Number of children at your 0.009 1.250 1.057 1.477
responsibility
Current cigarette smoking 0.016 2.302 1.167 4.539
Physical violence at home 0.015 14.398 1.674 123.809
Never works versus others 0.004 0.213 0.075 0.601 (yes vs. no)
APGAR score <0.001 0.833 0.763 0.909 APGAR score 0.004 0.892 0.826 0.964
Age in years 0.001 0.967 0.948 0.987 Fear of poverty score <0.001 1.202 1.106 1.305
Fear of poverty score <0.001 1.218 1.086 1.366 Being afraid of not accessing <0.001 2.269 1.424 3.616
Model 2: Correlates of PTSS symptoms, including insomnia as an treatment (yes vs. no)
independent variable (Nagelkerke R =0.392; Omnibus test <0.001; Sports during confinement 0.014 0.588 0.385 0.898
2
HL p-value=0.08) (yes vs. no)
Factor p‑value ORa 95% PTSS (yes vs. no) <0.001 3.295 1.949 5.571
confidence
interval of the Note: PTSS scale added in the model as an independent variable.
PTSS: Post-traumatic stress symptoms, APGAR: Adaptation,
ORa Partnership, Growth, Affection, and Resolve; IFDFW: The InCharge
Fear of COVID score <0.001 1.135 1.080 1.194 financial distress/financial well-being scale.
Female versus male gender <0.001 3.233 1.821 5.739
Current cigarette smoking 0.022 2.321 1.128 4.776 or sleep disorders (Huang & Zhao, 2020; Kokou-Kpolou
Current waterpipe smoking 0.020 2.911 1.180 7.182 et al., 2020; Rossi et al., 2020; Voitsidis et al., 2020) in
the general population during this pandemic, none has
Never works versus others 0.002 0.186 0.064 0.542 evaluated the direct relationships between the fear of the
Afraid of not accessing treatment 0.029 0.501 0.269 0.933 virus and PTSS and insomnia using a validated scale.
APGAR score <0.001 0.852 0.775 0.937 Some authors even pointed out that they could not identify
Age in years <0.001 0.961 0.940 0.982 which of the fear of the disease or the restrictive measures
Income level 0.019 1.563 1.076 2.271 imposed by governments were the direct causing factors
IFDWF wellness score <0.001 0.968 0.949 0.986 of mental health-related issues (Casagrande et al., 2020).
Insomnia (yes vs. no) <0.001 3.368 1.923 5.900 FOC could also be related to the concern of contracting
the disease or that it infects loved ones, in addition to
Model 3: Correlates of Insomnia (Nagelkerke R =0.247; Omnibus
2
test <0.001; HL p-value=0.488) fears of stigmatization and social exclusion in case of
Factor p‑value ORa 95% confirmed infection, being quarantined, losing one’s job,
Confidence etc. (Brooks et al., 2020) All these smothering ideas and
Interval of the fear experiences, further fueled by media overflow of
ORa information and misinformation, could potentially lead
Fear of COVID score 0.006 1.049 1.014 1.086 to irrational and unclear thoughts, which, in turn, would
Number of children at your 0.029 1.201 1.019 1.415 exacerbate underlying mental health problems and be
responsibility significant predictors of PTSS and insomnia.
Physical violence at home 0.006 20.292 2.354 174.947
(yes vs. no) 4.2. Economy, PTSS, and insomnia
APGAR score <0.001 0.863 0.801 0.930 In Lebanon, FOC was magnified by the fear of uncertainties
Fear of poverty score <0.001 1.220 1.124 1.325 related to the economy. Indeed, our results showed that
Being afraid of not accessing 0.006 1.920 1.209 3.047 financial hardship was significantly associated with higher
treatment (yes vs. no) levels of PTSS and insomnia, similar to previous findings
Sports during confinement 0.007 0.564 0.373 0.854 showing that people from low household incomes were
(yes vs. no) more likely to exhibit PTSS (Hawryluck et al., 2004).
(Cont’d...) Increased sleep difficulties were associated with fear of
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2023) 76 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.440