Page 13 - ITPS-5-2
P. 13
7 INNOSC Theranostics and Pharmacological Sciences, 2022, Vol. 5, No. 2 Dhokne et al.
opioidergic [69-72], imidazoline [11,73,74], a substantial role in the antinociceptive effect of
α2-adrenergic [75,76], and opioidergic sigma agmatine on NP. Hence, additional research is
receptors, which have been recently shown to have required on these predictions (Table 3).
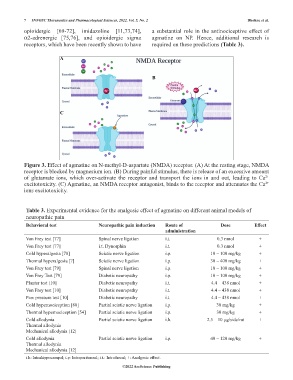
A
B
C
Figure 3. Effect of agmatine on N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor. (A) At the resting stage, NMDA
receptor is blocked by magnesium ion. (B) During painful stimulus, there is release of an excessive amount
of glutamate ions, which over-activate the receptor and transport the ions in and out, leading to Ca 2+
excitotoxicity. (C) Agmatine, an NMDA receptor antagonist, binds to the receptor and attenuates the Ca 2+
ions excitotoxicity.
Table 3. Experimental evidence for the analgesic effect of agmatine on different animal models of
neuropathic pain
Behavioral test Neuropathic pain induction Route of Dose Effect
administration
Von Frey test [77] Spinal nerve ligation i.t. 0.3 nmol +
Von Frey test [77] i.t. Dynorphin i.t. 0.3 nmol +
Cold hyperalgesia [78] Sciatic nerve ligation i.p. 10 – 100 mg/kg +
Thermal hyperalgesia [7] Sciatic nerve ligation i.p. 30 – 400 mg/kg +
Von Frey test [79] Spinal nerve ligation i.p. 10 – 100 mg/kg +
Von Frey Test [79] Diabetic neuropathy i.p. 10 – 100 mg/kg +
Plantar test [10] Diabetic neuropathy i.t. 4.4 – 438 nmol +
Von Frey test [10] Diabetic neuropathy i.t. 4.4 – 438 nmol +
Paw pressure test [10] Diabetic neuropathy i.t. 4.4 – 438 nmol +
Cold hypernociception [80] Partial sciatic nerve ligation i.p. 30 mg/kg +
Thermal hypernociception [54] Partial sciatic nerve ligation i.p. 30 mg/kg +
Cold allodynia Partial sciatic nerve ligation i.h. 2.5 – 10 μg/side/rat +
Thermal allodynia
Mechanical allodynia [12]
Cold allodynia Partial sciatic nerve ligation i.p. 40 – 120 mg/kg +
Thermal allodynia
Mechanical allodynia [12]
i.h: Intrahippocampal; i.p: Intraperitoneal; i.t.: Intrathecal; +: Analgesic effect.
©2022 AccScience Publishing