Page 45 - ITPS-7-1
P. 45
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Anticancer activity of cyanobacteria
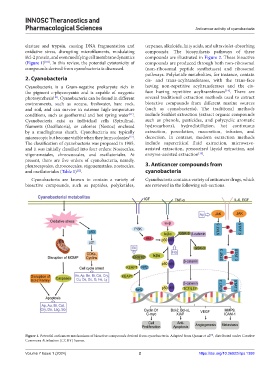
elastase and trypsin, causing DNA fragmentation and terpenes, alkaloids, fatty acids, and ultraviolet-absorbing
oxidative stress, disrupting microfilaments, modulating compounds. The biosynthesis pathways of these
Bcl-2 protein, and even modifying cell membrane dynamics compounds are illustrated in Figure 2. These bioactive
(Figure 1) [8,9] . In this review, the potential cytotoxicity of compounds are produced through both non-ribosomal
compounds derived from cyanobacteria is discussed. (non-ribosomal peptide synthetases) and ribosomal
pathways. Polyketide metabolites, for instance, contain
2. Cyanobacteria cis- and trans-acyltransferases, with the trans-face
Cyanobacteria is a Gram-negative prokaryote rich in having non-repetitive acyltransferases and the cis-
the pigment c-phycocyanin and is capable of oxygenic face having repetitive acyltransferases [14] . There are
photosynthesis . Cyanobacteria can be found in different several traditional extraction methods used to extract
[10]
environments, such as oceans, freshwater, bare rock, bioactive compounds from different marine sources
and soil, and can survive in extreme high-temperature (such as cyanobacteria). The traditional methods
conditions, such as geothermal and hot spring water . include Soxhlet extraction (extract organic compounds
[11]
Cyanobacteria exist as individual cells (Spirulina), such as phenols, pesticides, and polycyclic aromatic
filaments (Oscillatoria), or colonies (Nostoc) enclosed hydrocarbons), hydrodistillation, hot continuous
by a mucilaginous sheath. Cyanobacteria are typically extraction, percolation, maceration, infusion, and
microscopic but become visible when they form colonies . decoction. In contrast, modern extraction methods
[12]
The classification of cyanobacteria was proposed in 1985, include supercritical fluid extraction, microwave-
and it was initially classified into four orders: Nostocales, assisted extraction, pressurized liquid extraction, and
stigonematales, chroococcales, and oscillatoriales. At enzyme-assisted extraction [15] .
present, there are five orders of cyanobacteria, namely,
pleurocapsales, chroococcales, stigonematales, nostocales, 3. Anticancer compounds from
and oscillatoriales (Table 1) . cyanobacteria
[13]
Cyanobacteria are known to contain a variety of Cyanobacteria contain a variety of anticancer drugs, which
bioactive compounds, such as peptides, polyketides, are reviewed in the following sub-sections.
Figure 1. Potential anticancer mechanisms of bioactive compounds derived from cyanobacteria. Adapted from Qamar et al. , distributed under Creative
[9]
Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Volume 7 Issue 1 (2024) 2 https://doi.org/10.36922/itps.1388