Page 47 - ITPS-7-1
P. 47
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Anticancer activity of cyanobacteria
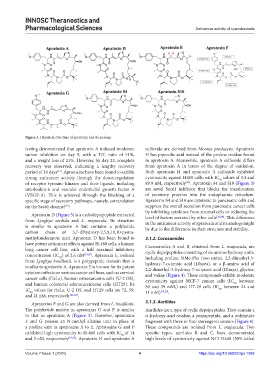
Figure 3. Chemical structure of apratoxin and its analogs.
testing demonstrated that apratoxin A induced moderate sulfoxide are derived from Moorea producens. Apratoxin
tumor inhibition on day 9, with a T/C ratio of 51%, H has pipecolic acid instead of the proline residue found
and a weight loss of 21%. However, by day 23, complete in apratoxin A. Meanwhile, apratoxin A sulfoxide differs
recovery was observed, indicating a lengthy recovery from apratoxin A in terms of the degree of oxidation.
period of 14 days . Apratoxins have been found to exhibit Both apratoxin H and apratoxin A sulfoxide exhibited
[17]
strong anticancer activity through the down-regulation cytotoxicity against H460 cells, with IC values of 3.4 and
50
[23]
of receptor tyrosine kinases and their ligands, including 89.9 nM, respectively . Apratoxin S4 and S10 (Figure 3)
interleukin-6 and vascular endothelial growth factor A are novel Sec61 inhibitor that blocks the translocation
(VEGF-A). This is achieved through the blocking of a of secretory proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum.
specific stage of secretory pathways, namely, cotranslation Apratoxin S4 and S10 are cytotoxic to pancreatic cells and
[18]
on the Sec61 channel . suppress the overall secretion from pancreatic cancer cells
by inhibiting cytokines from stromal cells or reducing the
Apratoxin D (Figure 3) is a cyclodepsipeptide extracted [18,24]
from Lyngbya sordida and L. majuscula. Its structure level of factors secreted by other cells . This difference
in the anticancer activity of apratoxin and its analogs might
is similar to apratoxin A but contains a polyketide be due to the differences in their structure and stability.
carbon chain of 3,7-dihydroxy-2,5,8,10,10-penta-
methylundecanoic acid. Apratoxin D has been found to 3.1.2. Cocosamides
have potent anticancer effects against H-460 cells, a human Cocosamides A and B, obtained from L. majuscula, are
lung cancer cell line, with a half maximal inhibitory cyclic depsipeptides consisting of six amino/hydroxy units,
concentration (IC ) of 2.6 nM [19,20] . Apratoxin E, isolated including proline, NMe-Phe (two units), 2,2-dimethyl-3-
50
from Lyngbya bouillonii, is a polypeptide domain that is hydroxy-7-octenoic acid (Dhoea), or a β-amino acid of
similar to apratoxin A. Apratoxin E is known for its potent 2,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxy-7-octynoic acid (Dhoya), glycine,
cytotoxic effects on various cancer cell lines, such as cervical and valine (Figure 4). These compounds exhibit moderate
cancer cells (HeLa), human osteosarcoma cells (U-2 OS), cytotoxicity against MCF-7 cancer cells (IC between
and human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells (HT29). Its 30 and 39 mM,) and HT-29 cells (IC between 24 and
50
IC values for HeLa, U-2 OS, and HT29 cells are 72, 59, 11 mM) [19,25] . 50
50
and 21 nM, respectively [21,22] .
Apratoxins F and G are also derived from L. bouillonii. 3.1.3. Aurilides
The polyketide moiety in apratoxins G and F is similar Aurilides are a type of cyclic depsipeptides. They contain a
to that in apratoxin A (Figure 3). However, apratoxins α-hydroxy-acid residue, a pentapeptide, and a polyketide
F and G possess an N-methyl alanine unit in place of fragment with three or four stereogenic centers (Figure 4).
a proline unit in apratoxins A to E. Apratoxins G and F These compounds are isolated from L. majuscula. Two
exhibited high cytotoxicity to H-460 cells with IC of 14 specific types, aurilides B and C, have demonstrated
50
and 2 nM, respectively [19,21] . Apratoxin H and apratoxin A high levels of cytotoxicity against NCI-H460 (50% lethal
Volume 7 Issue 1 (2024) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/itps.1388