Page 46 - ITPS-7-1
P. 46
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Anticancer activity of cyanobacteria
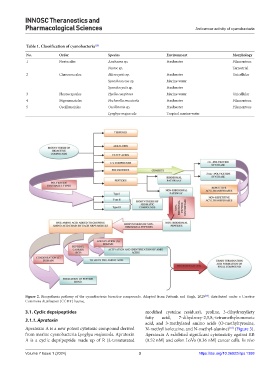
Table 1. Classification of cyanobacteria [13]
No. Order Species Environment Morphology
1 Nostocales Anabaena sp. Freshwater Filamentous
Nostoc sp. Terrestrial
2 Chroococcales Microcystis sp. Freshwater Unicellular
Synechococcus sp. Marine water
Synechocystis sp. Freshwater
3 Pleurocapsales Hyella caespitosa Marine water Unicellular
4 Stigonematales Fischerella muscicola Freshwater Filamentous
5 Oscillatoriales Oscillatoria sp. Freshwater Filamentous
Lyngbya majuscula Tropical marine water
[14]
Figure 2. Biosynthesis pathway of the cyanobacteria bioactive compounds. Adapted from Pattnaik and Singh, 2020 , distributed under a Creative
Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
3.1. Cyclic depsipeptides modified cysteine residues), proline, 3-dihydroxyliety
fatty acid, 7-dihydroxy-2,5,8,-tetramethylnonenoic
3.1.1. Apratoxin
acid, and 3-methylated amino acids (O-methyltyrosine,
Apratoxin A is a new potent cytotoxic compound derived N-methyl isoleucine, and N-methyl-alanine) (Figure 3).
[16]
from marine cyanobacteria Lyngbya majuscula. Apratoxin Apratoxin A exhibited significant cytotoxicity against KB
A is a cyclic depsipeptide made up of R (â-unsaturated (0.52 nM) and colon LoVo (0.36 nM) cancer cells. In vivo
Volume 7 Issue 1 (2024) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/itps.1388