Page 11 - ITPS-8-2
P. 11
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences AMPK in metabolism, energy and aging
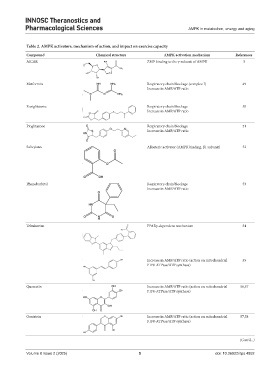
Table 2. AMPK activators, mechanism of action, and impact on exercise capacity
Compound Chemical structure AMPK activation mechanism References
AICAR ZMP binding to the γ-subunit of AMPK 5
Metformin Respiratory chain blockage (complex I) 49
Increase in AMP/ATP ratio
Rosiglitazone Respiratory chain blockage 50
Increase in AMP/ATP ratio
Pioglitazone Respiratory chain blockage 51
Increase in AMP/ATP ratio
Salicylates Allosteric activator (AMPK binding, β1 subunit) 52
Phenobarbital Respiratory chain blockage 53
Increase in AMP/ATP ratio
Telmisartan PPARγ-dependent mechanism 54
Increase in AMP/ATP ratio (action on mitochondrial 55
F1F0-ATPase/ATP synthase)
Quercetin Increase in AMP/ATP ratio (action on mitochondrial 56,57
F1F0-ATPase/ATP synthase)
Genistein Increase in AMP/ATP ratio (action on mitochondrial 57,58
F1F0-ATPase/ATP synthase)
(Cont’d...)
Volume 8 Issue 2 (2025) 5 doi: 10.36922/itps.4852