Page 39 - JCAU-5-3
P. 39
Journal of Chinese
Architecture and Urbanism Walkability evaluation of Beijing Old Town
historical buildings on both sides of the street. The overall processing, and then Pearson’s correlation test was used
trend is higher in the north and lower in the south, and to analyze the relationship between subjective feelings
higher in the middle and lower on both sides. The areas of walkability and specific objective data, such as street
with lower degree of protection are mainly distributed interface, street furniture, and street style. The results of
around the Temple (or Altar) of Agriculture, and the correlation analysis are shown in Table 2.
Temple of Heaven. The road accessibility around these The above are the results of correlation analysis of 13
two historical areas is low, and the visibility of the Temple independent variables and three dependent variables.
of Agriculture and the Temple of Heaven is insufficient. In general, the degree of correlation between the three
The sites surrounding the historic buildings are occupied subjective indexes and the 13 objective indicators are
by modern buildings, for instance, the Temple of relatively high, indicating the rationality of the selected
Agriculture and the Temple of Heaven are occupied by indicators. The sense of security has the strongest correlation
schools and hospitals, respectively (Han, 2005), and the with the degree of street maintenance management, and
protection of these historic buildings from the street is the feeling of comfort has a strong correlation with the
low. architectural quality, design aesthetics, and the street aspect
ratio. The main factor affecting the esthetics perception is
3.2. Analysis of subjective index of walkability
the degree of preservation of traditional features.
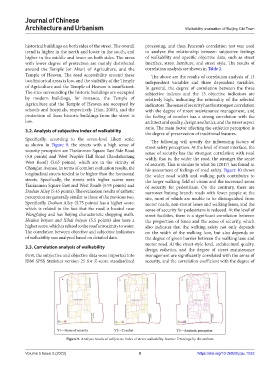
Specifically, according to the seven-level Likert scale, The following will specify the influencing factors of
as shown in Figure 9, the streets with a high sense of street safety perception. At the level of street interface, the
security perception are Tian’anmen Square East Side Road sense of security has the strongest correlation with road
(5.8 points) and West People’s Hall Road (Rendahuitang width, that is, the wider the road, the stronger the sense
West Road) (5.65 points), which are in the vicinity of of security. This is similar to what Su (2017) has found in
Chang’an Avenue. In terms of comfort evaluation results, the his assessment of feelings of road safety. Figure 10 shows
longitudinal streets tended to be higher than the horizontal the wider road width and walking path contributes to
streets. Specifically, the streets with higher scores were the larger walking field of vision and the increased sense
Tian’anmen Square East and West Roads (5.95 points) and of security for pedestrians. On the contrary, there are
Dashan Alley (5.45 points). The evaluation results of esthetic narrower hutong branch roads with fewer people at the
perception are generally similar to those of the previous two. site, most of which are unable to be distinguished from
Specifically, Dashan Alley (5.75 points) has a higher score, motor roads, non-motor lanes and walking lanes, and the
which is related to the fact that the road is located near sense of security for pedestrians is reduced. At the level of
Wangfujing and has Beijing characteristic shopping malls. street facilities, there is a significant correlation between
Houhai beiyan and Xihai beiyan (5.5 points) also have a the proportion of fence and the sense of security, which
higher score, which is related to the road’s proximity to water. also indicates that the walking safety not only depends
The correlation between objective and subjective indicators on the width of the walking lane, but also depends on
of walkability was analyzed based on detailed data. the degree of green barrier between the walking lane and
motor road. At the street-style level, architectural quality,
3.3. Correlation analysis of walkability
design esthetics, and the degree of street maintenance
First, the subjective and objective data were imported into management are significantly correlated with the sense of
IBM SPSS Statistics version 25 for Z-score standardized security, and the correlation coefficient with the degree of
Figure 9. Analysis results of subjective index of street walkability. Source: Drawings by the authors
Volume 5 Issue 3 (2023) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcau.1033