Page 50 - JCAU-5-4
P. 50
Journal of Chinese
Architecture and Urbanism Learning from the countryside
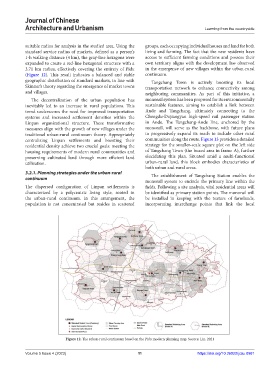
suitable radius for analysis in the studied area. Using the groups, each occupying individual houses and land for both
standard service radius of markets, defined as a person’s living and farming. The fact that the new residents have
1-h walking distance (4 km), the gray-line hexagons were access to sufficient farming conditions and possess their
expanded to create a red-line hexagonal structure with a own territory aligns with the development law observed
3.71 km radius, effectively covering the entirety of Pidu in the emergence of new villages within the urban-rural
(Figure 12). This result indicates a balanced and stable continuum.
geographic distribution of standard markets, in line with Tangchang Town is actively boosting its local
Skinner’s theory regarding the emergence of market towns transportation network to enhance connectivity among
and villages. neighboring communities. As part of this initiative, a
The decentralization of the urban population has monorail system has been proposed for its environmentally
inevitably led to an increase in rural populations. This sustainable features, aiming to establish a link between
trend underscores the need for improved transportation Ande and Tangchang, ultimately connecting to the
systems and increased settlement densities within the Chengdu-Dujiangyan high-speed rail passenger station
Linpan organizational structure. These transformative in Ande. The Tangchang-Ande line, anchored by the
measures align with the growth of new villages under the monorail, will serve as the backbone, with future plans
traditional urban-rural continuum theory. Appropriately to progressively expand its reach to include other rural
centralizing Linpan settlements and boosting their communities along the route. Figure 13 provides a detailed
residential density achieve two crucial goals: meeting the strategy for the smaller-scale square plot on the left side
housing requirements of modern rural communities and of Tangchang Town (the boxed area in frame A), further
preserving cultivated land through more efficient land elucidating this plan. Situated amid a multi-functional
utilization. urban-rural land, this block embodies characteristics of
both urban and rural areas.
3.2.1. Planning strategies under the urban-rural The establishment of Tangchang Station enables the
continuum
monorail system to encircle the primary line within the
The dispersed configuration of Linpan settlements is fields. Following a site analysis, vital residential areas will
characterized by a polycentric living style, rooted in be identified as primary station points. The monorail will
the urban-rural continuum. In this arrangement, the be installed in keeping with the texture of farmlands,
population is not concentrated but resides in scattered incorporating interchange points that link the local
Figure 12. The urban-rural continuum based on the Pidu modern planning map. Source: Lin, 2021
Volume 5 Issue 4 (2023) 11 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcau.0981