Page 74 - JCAU-7-1
P. 74
Journal of Chinese
Architecture and Urbanism Non-equilibrium territorial space use in PRD
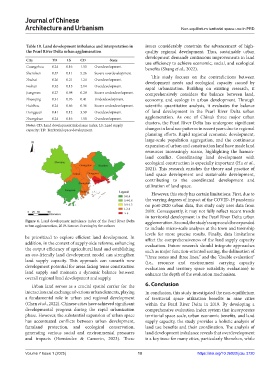
Table 10. Land development imbalance and interpretation in issues considerably constrain the advancement of high-
the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration quality regional development. Thus, sustainable urban
development demands continuous improvements in land
City TD LS CD State use efficiency to achieve economic, social, and ecological
Guangzhou 0.24 0.16 1.53 Overdevelopment benefits (Shang et al., 2022).
Shenzhen 0.57 0.11 5.26 Severe overdevelopment
This study focuses on the contradictions between
Zhuhai 0.26 0.21 1.24 Overdevelopment development needs and ecological capacity caused by
Foshan 0.32 0.15 2.14 Overdevelopment rapid urbanization. Building on existing research, it
Jiangmen 0.27 0.98 0.28 Severe underdevelopment comprehensively considers the balance between land,
Zhaoqing 0.31 0.76 0.41 Underdevelopment economy, and ecology in urban development. Through
Huizhou 0.24 0.66 0.36 Severe underdevelopment scientific quantitative analysis, it evaluates the balance
Dongguan 0.41 0.12 3.59 Overdevelopment of land development in the Pearl River Delta urban
Zhongshan 0.24 0.16 1.50 Overdevelopment agglomeration. As one of China’s three major urban
Notes: CD: Land development imbalance index; LS: Land supply clusters, the Pearl River Delta has undergone significant
capacity; TD: Territorial space development. changes in land use patterns in recent years due to regional
planning efforts. Rapid regional economic development,
large-scale population aggregation, and the continuous
expansion of urban and construction land have made land
resources increasingly scarce, highlighting the human-
land conflict. Coordinating land development with
ecological construction is especially important (Hu et al.,
2021). This research enriches the theory and practice of
land space development and sustainable development,
contributing to the coordinated development and
utilization of land space.
However, this study has certain limitations. First, due to
the varying degrees of impact of the COVID-19 pandemic
on post-2020 urban data, this study only uses data from
2019. Consequently, it may not fully reflect recent trends
in territorial development in the Pearl River Delta urban
Figure 4. Land development imbalance index of the Pearl River Delta agglomeration. Second, the study’s scope could be expanded
urban agglomeration, 2019. Source: Drawing by the authors
to include micro-scale analyses at the town and township
levels for more precise results. Finally, data limitations
be prioritized to explore efficient land development. In affect the comprehensiveness of the land supply capacity
addition, in the context of supply-side reforms, enhancing evaluation. Future research should integrate approaches
the output efficiency of agricultural land and establishing such as major function-oriented zoning, the delineation of
an eco-friendly land development model can strengthen “three zones and three lines,” and the “double evaluation”
land supply capacity. This approach can unearth new (i.e., resource and environment carrying capacity
development potential for areas facing tense construction evaluation and territory space suitability evaluation) to
land supply and maintain a dynamic balance between enhance the depth of the evaluation mechanism.
overall regional land development and supply.
Urban land serves as a crucial spatial carrier for the 6. Conclusion
interaction and exchange of various urban elements, playing In conclusion, this study investigated the non-equilibrium
a fundamental role in urban and regional development of territorial space utilization benefits in nine cities
(Chen et al., 2022). Chinese cities have achieved significant within the Pearl River Delta in 2019. By developing a
developmental progress during the rapid urbanization comprehensive evaluation index system that incorporates
phase. However, the substantial expansion of urban space territorial space scale, urban economic benefits, and land
has accentuated conflicts between urban development, supply capacity, the study provides a holistic analysis of
farmland protection, and ecological conservation, land use benefits and their coordination. The analysis of
generating various social and environmental pressures land development imbalance reveals that overdevelopment
and impacts (Hernández & Camerin, 2023). These is a key issue for many cities, particularly Shenzhen, while
Volume 7 Issue 1 (2025) 10 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcau.3720