Page 143 - JCAU-7-2
P. 143
Journal of Chinese
Architecture and Urbanism Urban features of PRD in online image
4.2.2. High-frequency texts
The frequency of text words reflects the main spatial carrier
and media communication content in the presentation of
town images. By analyzing the top-ranked high-frequency
words in the texts associated with each town (Table 7), it
is evident that the primary terms are “valley” (18.52%),
“tourism” (12.35%), “countryside” (8.64%), and “urban
areas/communities” (3.70%). The remaining words appear
in <3% of the texts, indicating that public perception is
strongly shaped by topography, behavior, and regional
features. Among second-ranked high-frequency words,
“culture,” “park/tourism,” and “landscape” are dominant,
reflecting that the public’s impressions of small towns are
shaped by cultural communication and the visual image of
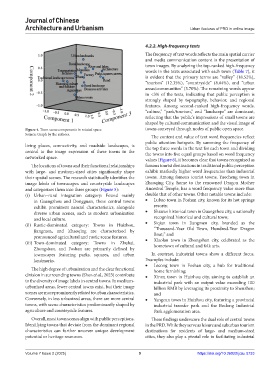
Figure 4. Town scene components in rotated space towns conveyed through nodes of public open space.
Source: Graph by the authors.
The content and value of text word frequencies reflect
public attention hotspots. By summing the frequency of
living places, connectivity, and roadside landscapes, is the top three words in the text for each town and dividing
central to the image expression of these towns in the the towns into five equal groups based on word frequency
networked space. values (Figure 6), it becomes clear that towns recognized as
The locations of towns and their functional relationships famous tourist destinations in traditional public perception
with large- and medium-sized cities significantly shape exhibit markedly higher word frequencies than industrial
their spatial scenes. The research statistically identifies the towns. Among famous tourist towns, Yuecheng town in
image labels of townscapes and countryside landscapes Zhaoqing City, home to the renowned Dragon Mother
and categorizes them into three groups (Figure 5): Ancestral Temple, has a word frequency value more than
(i) Urban–rural integration category: Found mainly double that of other towns. Other notable towns include:
in Guangzhou and Dongguan, these central towns • Lubao town in Foshan city, known for its hot springs
exhibit prominent natural characteristics, alongside resorts;
diverse urban scenes, such as modern urbanization • Shawan historical town in Guangzhou city, a nationally
and local culture. recognized historical and cultural town;
(ii) Rustic-dominated category: Towns in Huizhou, • Siqian town in Jiangmen city, branded as the
Jiangmen, and Zhaoqing are characterized by “Thousand-Year Old Town, Hundred-Year Dragon
pronounced agricultural and rustic scene features. Boat;” and
(iii) Town-dominated category: Towns in Zhuhai, • Xiaolan town in Zhongshan city, celebrated as the
Zhongshan, and Foshan are primarily defined by hometown of cultural and folk arts.
townscapes featuring parks, squares, and urban In contrast, industrial towns show a different focus.
landmarks. Examples include:
• Lecong town in Foshan city, a hub for traditional
The high degree of urbanization and the clear functional home furnishing;
division in surrounding towns (Shen et al., 2023) contribute • Xinxu town in Huizhou city, aiming to establish an
to the diversity of image labels in central towns. In medium- industrial park with an output value exceeding 100
urbanized areas, fewer central towns exist, but their image billion RMB by leveraging its proximity to Shenzhen;
scenes are more prominently related to urban characteristics. and
Conversely, in less urbanized areas, there are more central • Yangcun town in Huizhou city, featuring a provincial
towns, with scene characteristics predominantly shaped by industrial transfer park and the Bodong Industrial
agriculture and countryside features. Park agglomeration area.
Overall, most town scenes align with public perceptions. These findings underscore the dual role of central towns
Identifying towns that deviate from the dominant regional in the PRD. While they serve as leisure and suburban tourism
characteristics can further uncover unique development destinations for residents of large- and medium-sized
potential or heritage resources. cities, they also play a pivotal role in facilitating industrial
Volume 7 Issue 2 (2025) 9 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcau.5733