Page 42 - JCAU-7-2
P. 42
Journal of Chinese
Architecture and Urbanism Moisture damage in plastered heritage building
conditions, such as humidity and temperature. To the analysis. These data were combined with wall insolation
comprehensively analyze and compare sunlight’s effects on measurements to generate a comparative analysis chart of
buildings, detailed architectural models of the BCW and climatic conditions (Figure 13).
HGS buildings were created in Rhino software. These models The results indicate that sunlight exposure on the walls of
facilitated an in-depth sunlight analysis using Ladybug the BCW building peaked in June, with an average of 5.91 h
Tools. By conducting field measurements and utilizing of sunlight per day, whereas sunlight hours during January
Ladybug Tools components in Grasshopper, meteorological and December were nearly zero. Significant fluctuations
data from Shaoxing City were imported to simulate sunlight in daily sunlight duration were observed throughout the
hours, adjust parameters, and assess sunlight exposure under year, demonstrating clear seasonal variation (Annila et al.,
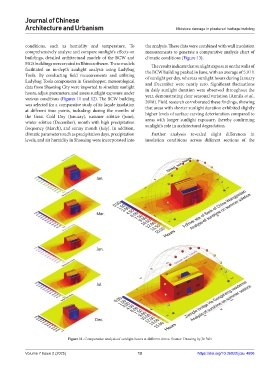
various conditions (Figures 11 and 12). The BCW building
was selected for a comparative study of its façade insolation 2018). Field research corroborated these findings, showing
that areas with shorter sunlight duration exhibited slightly
at different time points, including: during the months of
the Great Cold Day (January), summer solstice (June), higher levels of surface carving deterioration compared to
winter solstice (December), month with high precipitation areas with longer sunlight exposure, thereby confirming
frequency (March), and sunny month (July). In addition, sunlight’s role in architectural degradation.
climatic parameters such as precipitation days, precipitation Further analyses revealed slight differences in
levels, and air humidity in Shaoxing were incorporated into insolation conditions across different sections of the
Figure 11. Comparative analysis of sunlight hours at different times. Source: Drawing by Jie Wei
Volume 7 Issue 2 (2025) 12 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcau.4606