Page 32 - JCBP-1-1
P. 32
Journal of Clinical and
Basic Psychosomatics Relationship between PD and melanoma based on NHANES
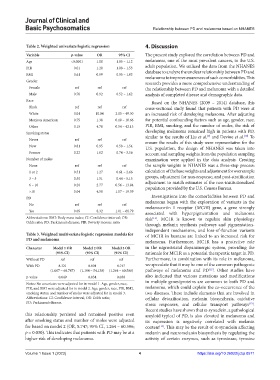
Table 2. Weighted univariate logistic regression 4. Discussion
Variable p‑value OR 95% CI The present study explored the correlation between PD and
Age <0.0001 1.08 1.05 – 1.12 melanoma, one of the most prevalent cancers, in the U.S.
PIR 0.01 1.28 1.08 – 1.53 adult population. We utilized the data from the NHANES
BMI 0.61 0.99 0.95 – 1.03 database to analyze the unclear relationship between PD and
melanoma to improve awareness of such comorbidities. This
Gender research provides a more comprehensive understanding of
Female ref ref ref the relationship between PD and melanoma with a detailed
Male 0.76 0.92 0.52 – 1.62 analysis of completed disease and demographic data.
Race Based on the NHANES (2009 – 2014) database, this
Black ref ref ref cross-sectional study found that patients with PD were at
White 0.01 10.04 2.05 – 49.30 an increased risk of developing melanoma. After adjusting
Mexican American 0.75 1.38 0.18 – 10.66 for potential confounding factors such as age, gender, race,
Other 0.15 4.78 0.54 – 42.13 PIR, BMI, smoking, and the number of moles, the risk of
Smoking status developing melanoma remained high in patients with PD,
[9]
[10]
Never ref ref ref similar to the results of Liu et al. and Devine et al. To
ensure the results of this study were representative for the
Now 0.81 0.95 0.58 – 1.54 U.S. population, the design of NHANES was taken into
Former 0.22 1.62 0.74 – 3.56 account and sampling weights from the population sampling
Number of moles examination were applied in the data analysis. Creating
None ref ref ref the sample weights in NHANES was a three-step process:
1 or 2 0.51 1.27 0.61 – 2.66 calculation of the base weights and adjustment for oversample
3 – 5 0.50 1.51 0.44 – 5.15 groups, adjustment for non-response, and post-stratification
6 – 10 0.20 2.77 0.56 – 13.84 adjustment to match estimates of the non-institutionalized
population provided by the U.S. Census Bureau.
>10 0.04 4.58 1.07 – 19.59
PD Investigations into the comorbidities between PD and
No ref ref ref melanoma began with the exploration of variants in the
melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) gene, a gene strongly
Yes 0.05 8.32 1.01 – 68.79 associated with hyperpigmentation and melanoma
Abbreviations: BMI: Body mass index; CI: Confidence interval; OR: risk . MC1R is known to regulate skin physiology
[11]
Odds ratio; PD: Parkinson’s disease; PIR: Poverty income ratio.
through melanin synthesis pathways and pigmentation-
independent mechanisms, and loss-of-function variants
Table 3. Weighted multivariate logistic regression models for of MC1R in humans are linked to an increased risk for
PD and melanoma melanoma. Furthermore, MC1R has a protective role
Character Model 1 OR Model 2 OR Model 3 OR in the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system, providing the
(95% CI) (95% CI) (95% CI) rationale for MC1R as a potential therapeutic target in PD.
Without PD ref ref ref Furthermore, in combination with its role in melanoma,
With PD 8.321 8.004 8.747 we speculate that it may be one of the common pathogenic
[12]
(1.007 – 68.787) (1.184 – 54.130) (1.264 – 60.506) pathways of melanoma and PD . Other studies have
p-value 0.049 0.034 0.030 also indicated that various mutations and modifications
in multiple genes/proteins are common to both PD and
Notes: No covariates were adjusted for in model 1. Age, gender, race,
PIR, and BMI were adjusted for in model 2. Age, gender, race, PIR, BMI, melanoma, which could explain the co-occurrence of the
smoking status, and number of moles were adjusted for in model 3. two diseases. These include elements that are involved in
Abbreviations: CI: Confidence interval; OR: Odds ratio; cellular detoxification, melanin biosynthesis, oxidative
PD: Parkinson’s disease. stress responses, and cellular transport pathways .
[13]
Recent studies have shown that α-synuclein, a pathological
this relationship persisted and remained positive even amyloid typical of PD, is also elevated in melanoma and
after smoking status and number of moles were adjusted its expression is negatively correlated with melanin
for based on model 2 (OR, 8.747; 95% CI, 1.264 – 60.506; content . This may be the result of α-synuclein affecting
[14]
p = 0.030). This indicates that patients with PD may be at a melanin and neuromelanin biosynthesis by regulating the
higher risk of developing melanoma. activity of certain enzymes, such as tyrosinase, tyrosine
Volume 1 Issue 1 (2023) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcbp.0571