Page 12 - JCBP-1-2
P. 12
Journal of Clinical and
Basic Psychosomatics Melatonin for dementia therapy
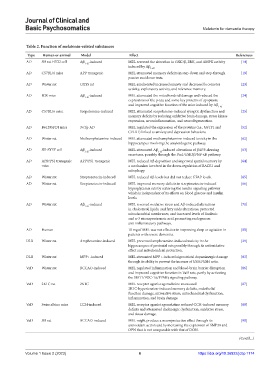
Table 2. Function of melatonin‑related substances
Type Human or animal Model Effect References
AD SD rat HT22 cell Aβ -induced MEL reversed the alteration in GSK3β, ERK, and AMPK activity [14]
1-42
induced by Aβ .
1-42
AD C57BL/6 mice APP transgenic MEL attenuated memory deficits in step-down and step-through [19]
passive avoidance tests.
AD Wister rat OXYS rat MEL ameliorated increased anxiety and decreased locomotor [23]
activity, exploratory activity, and reference memory.
AD ICR mice Aβ 1-42 -induced MEL attenuated the mitochondrial damage and reduced the [24]
expressions of the p-tau and some key proteins of apoptosis,
and improved cognitive function of the mice induced by Aβ .
1-42
AD C57BL/6 mice Scopolamine-induced MEL attenuated scopolamine-induced synaptic dysfunction and [25]
memory deficits by reducing oxidative brain damage, stress kinase
expression, neuroinflammation, and neurodegeneration.
AD B6129SF2/J mice 3×Tg-AD MEL regulated the expression of the proteins (i.e., GSTP1 and [52]
CPLX1) linked to anxiety and depression behaviors.
AD Wister rat Methamphetamine-induced MEL attenuated methamphetamine-induced toxicity in the [62]
hippocampus involving the amyloidogenic pathway.
AD SH-SY5Y cell Aβ 1-42 -induced MEL attenuated Aβ 1-42 -induced alterations of βAPP-cleaving [63]
secretases, possibly through the Pin1/GSK3β/NF-κB pathway.
AD APP/PS1 transgenic APP/PS1 transgenic MEL reduced Aβ deposition and improved spatial memory by [64]
mice a mechanism involved in the down-regulation of BACE1 and
mitophagy.
AD Wister rat Streptozotocin-induced MEL reduced Aβ levels but did not reduce GFAP levels. [65]
AD Wister rat Streptozotocin-induced MEL improved memory deficits in streptozotocin-induced [66]
hyperglycemia rats by restoring the insulin signaling pathway
which is independent of its effects on blood glucose and insulin
levels.
AD Wister rat Aβ -induced MEL reversed oxidative stress and Aβ-induced alterations [71]
1-42
in cholesterol, lipids, and fatty acids alterations, protected
mitochondrial membranes, and increased levels of linolenic
and n-3 eicosapentaenoic acid, promoting endogenous
anti-inflammatory pathways.
AD Human 10 mg of MEL was not effective in improving sleep or agitation in [80]
patients with severe dementia.
DLB Wister rat Amphetamine-induced MEL prevented amphetamine-induced toxicity in the [29]
hippocampus of postnatal rats possibly through its antioxidative
effect and mitochondrial protection.
DLB Wister rat MPP+-induced MEL attenuated MPP+-induced nigrostriatal dopaminergic damage [83]
through its ability to prevent the increase of GSSG/GSH ratio.
VaD Wister rat BCCAO-induced MEL regulated inflammation and blood-brain barrier disruption [86]
and improved cognitive function in VaD rats, partly by activating
the SIRT1/PGC-1α/PPARγ signaling pathway.
VaD 2K1C rat 2K1C MEL receptor agonist agomelatine attenuated [87]
2K1C-hypertension-induced memory deficits, endothelial
function damage, nitrosative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction,
inflammation, and brain damage.
VaD Swiss albino mice CCH-induced MEL receptor agonist agomelatine reduced CCH-induced memory [89]
deficits and attenuated cholinergic dysfunction, oxidative stress,
and tissue damage.
VaD SD rat BCCAO-induced MEL might produce a neuroprotective effect through its [90]
antioxidant action and by increasing the expression of SMP30 and
OPN that is not comparable with that of DON.
(Cont’d...)
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcbp.1174