Page 13 - JCBP-1-2
P. 13
Journal of Clinical and
Basic Psychosomatics Melatonin for dementia therapy
Table 2. (Continued)
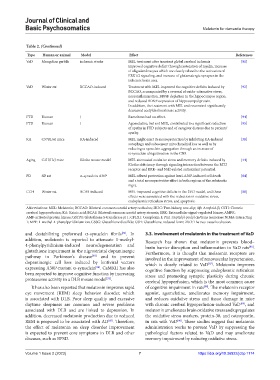
Type Human or animal Model Effect References
VaD Mongolian gerbils ischemic stroke MEL treatment after transient global cerebral ischemia [91]
improved cognitive deficit through restoration of myelin, increase
of oligodendrocytes which are closely related to the activation of
ERK1/2 signaling, and increase of glutamatergic synapses in the
ischemic brain area.
VaD Wister rat BCCAO-induced Treatment with MEL improved the cognitive deficits induced by [92]
BCCAO, accompanied by a reversal of oxido-nitrosative stress,
neuroinflammation, BDNF depletion in the hippocampus region,
and reduced BDNF expression of hippocampal protein.
In addition, the treatment with MEL and resveratrol significantly
decreased acetylcholinesterase activity.
FTD Human / Ramelteon had no effect. [94]
FTD Human / Agomelatine, but not MEL, contributed to a significant reduction [95]
of apathy in FTD subjects and of caregiver distress due to patients’
apathy.
KA C57BL/6J mice KA-induced MEL might exert its neuroprotection by inhibiting KA-induced [38]
autophagy and subsequent mitochondrial loss as well as by
reducing α-synuclein aggregation through an increase of
α-synuclein ubiquitination in the CNS.
Aging C3H/HeJ mice Klotho mouse model MEL attenuated oxidative stress and memory deficits induced by [44]
Klotho deficiency through signaling interaction between the MT2
receptor and ERK- and Nrf2-related antioxidant potential.
PD SD rat α-synuclein A30P MEL offered protection against lenti-A30P-induced cell death [84]
and a total neuroprotective effect in both regions of the substantia
nigra.
CCH Wister rat BCAS-induced MEL improved cognitive deficits in the 2VO model, and these [88]
effects were associated with the reduction in oxidative stress,
endoplasmic reticulum stress, and apoptosis.
Abbreviations: MEL: Melatonin; BCCAO: Bilateral common carotid artery occlusion; 2K1C: Two-kidney, one-clip; Aβ: Amyloid-β; CCH: Chronic
cerebral hypoperfusion; KA: Kainic acid; BCAS: Bilateral common carotid artery stenosis; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; AMPK:
AMP-activated protein kinase; GSTP1: Glutathione S-transferase pi 1; CPLX1: Complexin 1; Pin1: Peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase NIMA-interacting
1; MPP: 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion; GSSG: Glutathione disulfide; GSH: Glutathione, reduced form; 2VO: The two-vessel occlusion.
and destabilizing preformed α-synuclein fibrils . In 3.3. Involvement of melatonin in the treatment of VaD
[82]
addition, melatonin is reported to attenuate 1-methyl- Research has shown that melatonin prevents blood–
4-phenylpyridinium-induced neurodegeneration and brain barrier disruption and inflammation in VaD rats .
[86]
glutathione impairment in the nigrostriatal dopaminergic Furthermore, it is thought that melatonin receptors are
[83]
pathway in Parkinson’s disease and to prevent involved in the improvement of renovascular hypertension,
dopaminergic cell loss induced by lentiviral vectors which is closely related to VaD . Melatonin improves
[87]
expressing A30P-mutant α-synuclein . CaMKII has also cognitive function by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum
[84]
been reported to improve cognitive function by increasing stress and promoting synaptic plasticity during chronic
proteasome activity in a DLB mouse model . cerebral hypoperfusion, which is the most common cause
[32]
It has also been reported that melatonin improves rapid of cognitive impairment in rats . The melatonin receptor
[88]
eye movement (REM) sleep behavior disorder, which agonist, agomelatine, ameliorates memory impairment,
is associated with DLB. Poor sleep quality and excessive and reduces oxidative stress and tissue damage in mice
daytime sleepiness are common and severe problems with chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-induced VaD , and
[89]
associated with DLB and are linked to depression. In melatonin ameliorates brain oxidative stress and upregulates
addition, decreased melatonin production due to reduced the oxidative stress markers, protein-30, and osteopontin,
[90]
[85]
REM is proposed to be associated with AD . Therefore, in rats with VaD . These studies suggest that melatonin
the effect of melatonin on sleep disorder improvement administration works to prevent VaD by suppressing the
is expected to prevent core symptoms in DLB and other pathological factors related to VaD and may ameliorate
diseases, such as BPSD. memory impairment by reducing oxidative stress.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2023) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcbp.1174