Page 13 - JCBP-2-1
P. 13
Journal of Clinical and
Basic Psychosomatics MRI and functional constipation
A
B C
D E
[28]
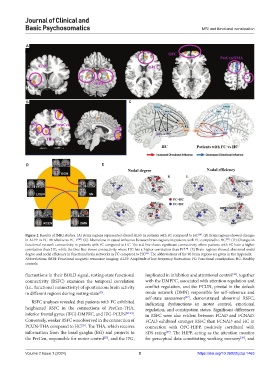
Figure 2. Results of fMRI studies. (A) Brain regions represented altered ALFF in patients with FC compared to HC . (B) Brain regions showed changes
in ALFF in FC_M relative to FC_F . (C) Alterations in causal influence between brain regions in patients with FC compared to HC . (D) Changes in
[28]
[30]
functional network connectivity in patients with FC compared to HC. The red line shows significant connectivity where patients with FC have a higher
correlation than HC, while the blue line shows connectivity where HC has a higher correlation than FC . (E) Brain regions showed abnormal nodal
[34]
[34]
degree and nodal efficiency in functional brain networks in FC compared to HC . The abbreviations of the 90 brain regions are given in the Appendix.
Abbreviations: fMRI: Functional magnetic resonance imaging; ALFF: Amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation; FC: Functional constipation; HC: Healthy
controls.
fluctuations in their BOLD signal, resting-state functional implicated in inhibition and attentional control , together
[36]
connectivity (RSFC) examines the temporal correlation with the DMPFC, associated with attention regulation and
(i.e., functional connectivity) of spontaneous brain activity conflict regulation, and the PCUN, pivotal in the default
in different regions during resting-state . mode network (DMN) responsible for self-reference and
[33]
self-state assessment , demonstrated abnormal RSFC,
[37]
RSFC analyses revealed that patients with FC exhibited indicating dysfunctions in motor control, emotional
heightened RSFC in the connections of PreCen-THA, regulation, and constipation status. Significant differences
inferior frontal gyrus (IFG)-DMPFC, and IFG-PCUN [29,34] . in RSFC were also evident between FCAD and FCNAD.
Conversely, weaker RSFC was observed in the connection of FCAD exhibited stronger RSFC than FCNAD and HC in
PCUN-THA compared to HC . The THA, which receives connection with OFC-HIPP, positively correlated with
[29]
information from the basal ganglia (BG) and projects to SDS rating . The HIPP, acting as the attention monitor
[29]
the PreCen, responsible for motor control , and the IFG, for perceptual data constituting working memory , and
[38]
[35]
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2024) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcbp.1463