Page 72 - JCBP-3-2
P. 72
Journal of Clinical and
Basic Psychosomatics Evaluation of biopsychosocial factors
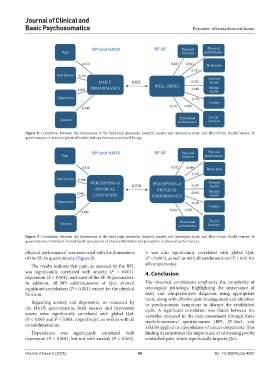
Figure 8. Correlation between the dimensions of the brief pain inventory, hospital anxiety and depression scale, and Short-Form Health Survey 36
questionnaires in terms of physical health (daily performance and well-being).
Figure 9. Correlation between the dimensions of the brief pain inventory, hospital anxiety and depression scale, and Short-Form Health Survey 36
questionnaires in terms of mental health (perception of physical limitation and perception of physical performance).
physical performance” was associated with the dimensions It was also significantly correlated with global QoL
of the SF-36 questionnaire (Figure 9). (P < 0.001), as well as with all subdimensions (P < 0.01 for
The results indicate that pain, as assessed by the BPI, all comparisons).
was significantly correlated with anxiety (P < 0.001), 4. Conclusion
depression (P < 0.001), and most of the SF-36 parameters.
In addition, all BPI subdimensions of QoL showed The observed correlations emphasize the complexity of
significant correlations (P < 0.001), except for the physical oncological pathology, highlighting the importance of
function. early and comprehensive diagnosis using appropriate
tools, along with effective pain management and attention
Regarding anxiety and depression, as measured by to psychosomatic symptoms to disrupt the established
the HADS questionnaire, both anxiety and depression cycle. A significant correlation was found between the
scores were significantly correlated with global QoL variables analyzed in the pain assessment through three
(P < 0.003 and P < 0.001, respectively), as well as with all multidimensional questionnaires (BPI, SF-36v2, and
its subdimensions. HADS) applied to a population of cancer outpatients. This
Dependence was significantly correlated with finding demonstrates the importance of addressing poorly
depression (P < 0.001), but not with anxiety (P = 0.060). controlled pain, which significantly impacts QoL.
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2025) 66 doi: 10.36922/jcbp.4097