Page 86 - JCTR-10-1
P. 86
82 Covre et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2024; 10(1): 78-84
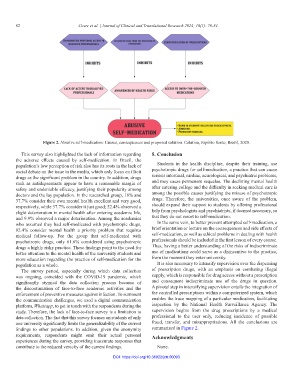
Figure 2. Abusive self-medication: Causes, consequences and proposed solution. Colatina, Espírito Santo, Brazil, 2020.
This survey also highlighted the lack of information regarding 5. Conclusion
the adverse effects caused by self-medication. In Brazil, the
population’s low perception of risk also has its roots in the lack of Students in the health discipline, despite their training, use
social debate on the issue in the media, which only focus on illicit psychotropic drugs for self-medication, a practice that can cause
drugs as the significant problem in the country. In addition, drugs serious intestinal, cardiac, neurological, and psychiatric problems,
such as antidepressants appear to have a reasonable margin of and may cause permanent sequelae. The declining mental health
safety and undeniable efficacy, justifying their popularity among after entering college and the difficulty in seeking medical care is
doctors and the lay population. In the researched group, 18% and among the possible causes justifying the misuse of psychotropic
37.7% consider their own mental health excellent and very good, drugs. Therefore, the universities, once aware of the problem,
respectively, while 37.7% consider it just good; 52.4% observed a should expand their support to students by offering professional
slight deterioration in mental health after entering academic life, help from psychologists and psychiatrists, if deemed necessary, so
and 9.9% observed a major deterioration. Among the academics that they do not resort to self-medication.
who assumed they had self-medicated with psychotropic drugs, In the same vein, to better prevent attempted self-medication, a
92.4% consider mental health a priority problem that requires brief orientation or lecture on the consequences and side effects of
medical follow-up. For the group that self-medicated with self-medication, as well as ethical problems in dealing with health
psychotropic drugs, only 61.6% considered using psychotropic professionals should be included in the first lesson of every course.
drugs a highly risky practice. These findings point to the need for Thus, having a better understanding of the risks of indiscriminate
better attention to the mental health of the university students and use of medications could serve as a disincentive to the practice,
more education regarding the practice of self-medication for the from the moment they enter university.
population as a whole. It is also necessary to intensify supervision over the dispensing
The survey period, especially during which data collection of prescription drugs, with an emphasis on combating illegal
was ongoing, coincided with the COVID-19 pandemic, which supply, which is responsible for drug access without a prescription
significantly stymied the data collection process because of and consequent indiscriminate use of the drugs in question.
the discontinuation of face-to-face academic activities and the A pivotal step in intensifying supervision entails the integration of
enforcement of preventive measures against infection. To surmount the controlled prescriptions within a computerized system, which
the communication challenges, we used a digital communication enables the trace mapping of a particular medication, facilitating
platform, Whatsapp, to get in touch with the respondents during the inspection by the National Health Surveillance Agency. The
study. Therefore, the lack of face-to-face survey is a limitation to supervision begins from the drug prescriptions by a medical
data collection. The fact that this survey focuses on students of only professional to the user only, reducing incidence of possible
one university significantly limits the generalizability of the current fraud, transfer, and misappropriations. All the conclusions are
findings to other populations. In addition, given the anonymity summarized in Figure 2.
requirements, respondents might omit their actual personal Acknowledgments
experiences during the survey, providing inaccurate responses that
contribute to the reduced veracity of the current findings. None.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36922/jctr.00093