Page 31 - JCTR-10-2
P. 31
Abtahi et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2024; 10(2): 119-140 125
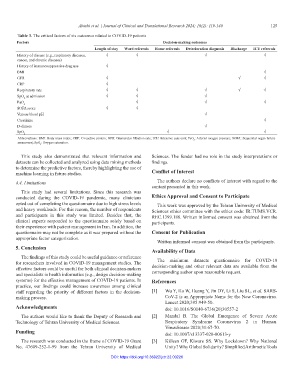
Table 3. The critical factors of six outcomes related to COVID-19 patients
Factors Decision‑making outcomes
Length of stay Ward referrals Home referrals Deterioration diagnosis Discharge ICU referrals
History of disease (e.g., respiratory diseases, √ √ √ √
cancer, and chronic diseases)
History of immunosuppressive drug use √
BMI √
GFR √ √ √
CRP √
Respiratory rate √ √ √ √ √
SpO at admission √ √ √
2
PaO √ √ √
2
SOFA score √ √
Venous blood pH √
Creatinine √
D-dimers √
SpO √ √
2
Abbreviations: BMI: Body mass index; CRP: C-reactive protein; GFR: Glomerular filtration rate; ICU: Intensive care unit; PaO : Arterial oxygen pressure; SOFA: Sequential organ failure
2
assessment; SpO : Oxygen saturation.
2
This study also demonstrated that relevant information and Sciences. The funder had no role in the study interpretations or
datasets can be collected and analyzed using data mining methods findings.
to determine the predictive factors, thereby highlighting the use of
machine learning in future studies. Conflict of Interest
4.4. Limitations The authors declare no conflicts of interest with regard to the
content presented in this work.
This study had several limitations. Since this research was
conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic, many clinicians Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
opted out of completing the questionnaire due to high stress levels This work was approved by the Tehran University of Medical
and heavy workloads. For this reason, the number of respondents Sciences ethics committee with the ethics code: IR.TUMS.VCR.
and participants in this study was limited. Besides that, the REC.1399.188. Written informed consent was obtained from the
clinical experts responded to the questionnaire solely based on participants.
their experience with patient management in Iran. In addition, the
questionnaire may not be complete as it was prepared without the Consent for Publication
appropriate factor categorization.
Written informed consent was obtained from the participants.
5. Conclusion
Availability of Data
The findings of this study could be useful guidance or reference
for researchers involved in COVID-19 management studies. The The minimum datasets questionnaire for COVID-19
effective factors could be useful for both clinical decision-makers decision-making and other relevant data are available from the
and specialists in health informatics (e.g., design decision-making corresponding author upon reasonable request.
systems) for the effective management of COVID-19 patients. In References
practice, our findings could increase awareness among clinical
staff regarding the priority of different factors in the decision- [1] Wu Y, Ho W, Huang Y, Jin DY, Li S, Liu SL, et al. SARS-
making process. CoV-2 is an Appropriate Name for the New Coronavirus.
Lancet 2020;395:949-50.
Acknowledgments doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30557-2
The authors would like to thank the Deputy of Research and [2] Mandal B. The Global Emergence of Severe Acute
Technology of Tehran University of Medical Sciences. Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 in Human.
Virusdisease 2020;31:67-70.
Funding doi: 10.1007/s13337-020-00613-y
The research was conducted in the frame of COVID-19 Grant [3] Killeen GF, Kiware SS. Why Lockdown? Why National
No. 47609-252-1-99 from the Tehran University of Medical Unity? Why Global Solidarity? Simplified Arithmetic Tools
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36922/jctr.22.00226