Page 51 - JCTR-10-5
P. 51
Arnold and Arm | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2024;10(5):307-316 313
8 weeks of weekly topical PMVT treatments, the defect was peripheral neuropathy. Vascular changes, including endothelial
completely filled and 99% epithelialized. After 10 weeks, the dysfunction, hyperpermeability, decreased blood flow, and
defect was closed, and PMVT treatment was discontinued. tissue hypoxia, can directly result from hyperglycemia. Vascular
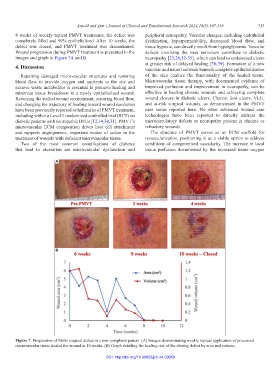
Wound progression during PMVT treatment is presented in the defects involving the vasa nervorum contribute to diabetic
images and graph in Figure 7A and B. neuropathy [23,26,32-35], which can lead to undetected ulcers
at greater risk of delayed healing [36-39]. Formation of a new
4. Discussion vascular and neural network beneath complete epithelialization
Repairing damaged microvascular structures and restoring of the skin enables the functionality of the healed tissue.
blood flow to provide oxygen and nutrients to the site and Microvascular tissue therapy, with documented evidence of
remove waste metabolites is essential to promote healing and improved perfusion and improvement in neuropathy, can be
minimize tissue breakdown in a newly epithelialized wound. effective in healing chronic wounds and achieving complete
Reversing the stalled wound environment, restoring blood flow, wound closure in diabetic ulcers, Charcot foot ulcers, VLU,
and changing the trajectory of healing toward wound resolution and at-risk surgical wounds, as demonstrated in the PMVT
have been previously reported as hallmarks of PMVT treatment, case series reported here. No other advanced wound care
including within a Level 1 randomized controlled trial (RCT) on technologies have been reported to directly address the
diabetic patients with neuropathic DFUs [12,14,30,31]. PMVT’s microcirculatory defects or neuropathy present in chronic or
microvascular ECM composition drives host cell attachment refractory wounds.
and supports angiogenesis, important modes of action in the The structure of PMVT serves as an ECM scaffold for
treatment of wounds with deficient microvascular tissue. revascularization, positioning it as a viable option to address
Two of the most common complications of diabetes conditions of compromised vascularity. The increase in local
that lead to ulceration are microvascular dysfunction and tissue perfusion documented by the increased tissue oxygen
A
B
Figure 7. Progression of Mohs surgical defect in a non-compliant patient. (A) Images demonstrating weekly topical application of processed
microvascular tissue healed the wound in 10 weeks. (B) Graph detailing the healing rate of the closing defect by area and volume.
DOI: http://doi.org/10.36922/jctr.24.00059