Page 48 - JCTR-10-5
P. 48
310 Arnold and Arm | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2024;10(5):307-316
standard dressings, collagen, offloading, hyperbaric oxygen, diabetic patients worldwide [19,20]. The most common form
and intravenous (IV) antibiotics, the patient presented with is peripheral neuropathy, where peripheral nerves are damaged
a refractory wound of 7 cm in area and 2 cm deep, with or destroyed, resulting in loss of feeling and/or sensations of
2
exposed bone and chronic osteomyelitis. He was treated with pain or paresthesia, primarily in the extremities [21,22]. While
weekly applications of topical PMVT along with additional IV the cause of diabetic neuropathy is not fully understood, the
antibiotics. High-resolution photos of the wound progression combination of vascular and neural components is recognized as
and a graph depicting wound area and volume reduction are important elements in its pathophysiology. Diabetic neuropathy
displayed in Figure 2A and B. After just one treatment with is a progressive disease, in which tissue-level structural changes
PMVT, over 80% of the wound volume had been replaced with occur in the patient’s peripheral microvascular system [23-25].
new tissue. After six applications, the wound size had reduced The first pathological changes observed are the narrowing
by more than 99%, so PMVT treatment was discontinued. The of the microvascular vessels and alteration of the normal
ulcer fully closed after four additional weeks with standard care local microvascular tissue network. As diabetic neuropathy
and remained healed at his most recent visit 9 months following progresses, neuronal dysfunction and reduction in peripheral
closure. nerve function have been demonstrated to correlate with the
3.2. Case 2: Stimulation of perfusion and healing using PMVT development of blood vessel abnormalities. Neuronal ischemia
is a well-established characteristic of diabetic neuropathy [26].
in a non-healing Charcot diabetic foot ulcer
Charcot foot, a severe complication of peripheral neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is one of the most frequent complications that can damage the bones, joints, and soft tissue in the foot,
of diabetes, experienced by 50 – 60% of the 389 million is known to result in the formation of non-healing ulcers [27].
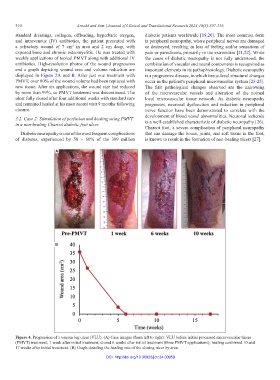
A
B
Figure 4. Progression of a venous leg ulcer (VLU). (A) Case images (from left to right): VLU before initial processed microvascular tissue
(PMVT) treatment; 1 week after initial treatment; closed 6 weeks after initial treatment (three PMVT applications); healing confirmed 10 and
17 weeks after initial treatment. (B) Graph detailing the healing rate of the closing ulcer by area.
DOI: http://doi.org/10.36922/jctr.24.00059