Page 29 - JCTR-10-6
P. 29
Cordeiro et al.ǀ Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2024; 10(6): 334-342 339
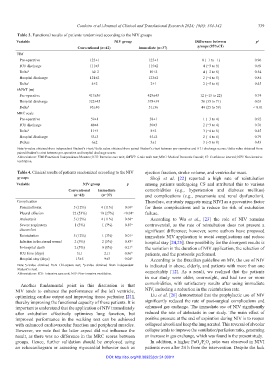
Table 3. Functional results of patients randomized according to the NIV groups
Variable NIV group Difference between p a
Conventional (n=42) Immediate (n=37) groups (95%CI)
FIM
Pre-operative 125±1 125±1 0 (−1 to −1) 0.96
ICU discharge 111±3 115±2 4 (−3 to 9) 0.69
Delta b 14±2 10±2 4 (−2 to 8) 0.54
Hospital discharge 121±2 123±2 2 (−4 to 5) 0.84
Delta c 4±2 2±1 2 (−5 to 6) 0.45
6MWT (m)
Pre-operative 417±36 429±43 12 (−15 to 22) 0.74
Hospital discharge 322±45 378±39 56 (35 to 71) 0.03
Delta b 95±40 51±36 44 (25 to 59) < 0.01
MRC scale
Pre-operative 59±1 58±1 1 (−3 to 4) 0.92
ICU discharge 48±4 50±3 2 (−3 to 4) 0.76
Delta b 11±3 8±2 3 (−4 to 8) 0.45
Hospital discharge 53±3 55±2 2 (−4 to 6) 0.79
Deltac 6±2 3±1 3 (−5 to 8) 0.43
b
c
Note: p-value obtained from independent Student’s t-test; delta value obtained from paired Student’s t-test between pre-operative and ICU discharge scores; delta value obtained from
a
paired Student’s t-test between pre-operative and hospital discharge scores.
Abbreviations: FIM: Functional Independence Measure; ICU: Intensive care unit; 6MWT: 6-min walk test; MRC: Medical Research Council; CI: Confidence interval; NIV: Non-invasive
ventilation.
Table 4. Clinical results of patients randomized according to the NIV ejection fraction, stroke volume, and ventricular mass.
groups Shoji et al. [22] reported a high rate of reintubation
Variable NIV group p among patients undergoing CS and attributed this to various
Conventional Immediate comorbidities (e.g., hypertension and diabetes mellitus)
(n=42) (n=37) and complications (e.g., pneumonia and renal dysfunction).
Complication Therefore, our study suggests using NIVI as a preventive factor
Pneumothorax 5 (12%) 4 (11%) 0.69 a for these complications and to reduce the risk of extubation
Pleural effusion 22 (53%) 10 (27%) <0.01 a failure.
Atelectasis 5 (12%) 4 (11%) 0.68 a According to Wu et al., [23] the role of NIV remains
Severe respiratory 1 (3%) 1 (3%) 0.87 a controversial, as the rate of reintubation does not present a
discomfort significant difference; however, some authors have proposed
Reintubation 5 (12%) 1 (3%) 0.01 a immediate NIV application to avoid complications and reduce
Infection in the sternal wound 2 (5%) 2 (5%) 0.83 a hospital stay [24,25]. One possibility for the divergent results is
In-hospital death 2 (5%) 0 (0%) 0.21 b the variation in the duration of NIV application, the selection of
ICU time (days) 3±1 2±1 0.86 b patients, and the protocols performed.
Hospital stay (days) 13±5 9±3 0.04 b According to the Brazilian guideline on MV, the use of NIV
Note: p-value obtained from Chi-square test; p-value obtained from independent is indicated in obese, elderly, and patients with more than one
a
b
Student’s t-test.
Abbreviations: ICU: Intensive care unit; NIV: Non-invasive ventilation. comorbidity [12]. As a result, we realized that the patients
in our study were older, overweight, and had two or more
Another fundamental point in this discussion is that comorbidities, with satisfactory results after using immediate
NIV tends to enhance the performance of the left ventricle, NIV, including a reduction in the reintubation rate.
optimizing cardiac output and improving tissue perfusion [21], Liu et al. [26] demonstrated that the prophylactic use of NIV
thereby improving the functional capacity of these patients. It is significantly reduced the rate of post-surgical complications and
important to understand that the application of NIV immediately enhanced gas exchange. The immediate use of NIV significantly
after extubation effectively optimizes lung function, but reduced the rate of atelectasis in our study. The main effect of
improved performance in the walking test can be achieved positive pressure at the end of expiration during NIV is to reopen
with enhanced cardiovascular function and peripheral muscles. collapsed alveoli and keep the lung aerated. This reversal of alveolar
However, we note that the latter aspect did not influence the collapse tends to improve the ventilation/perfusion ratio, generating
result, as there was no difference in the MRC scores between an increase in gas exchange, which was found in the present study.
groups. Hence, further validation should be employed using In addition, a higher PaO /F O ratio was observed in NIVI
I
2
2
an echocardiogram or assessing myocardial behavior such as patients even after 24 h from the intervention. Despite the lack
DOI: http://doi.org/10.36922/jctr.24.00011