Page 30 - JCTR-10-6
P. 30
340 Cordeiro et al.ǀ Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2024; 10(6): 334-342
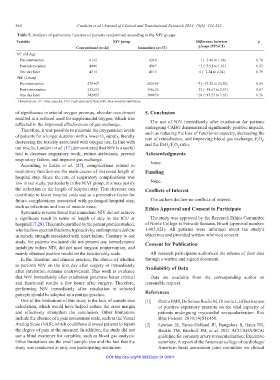
Table 5. Analysis of pulmonary function of patients randomized according to the NIV groups
Variable NIV group Difference between p
Conventional (n=42) Immediate (n=37) groups (95%CI)
VC (mL/kg)
Pre-intervention 61±5 62±6 −1 (−3.46 to 1.46) 0.78
Post-intervention 44±6 45±7 −1 (−3.91 to 1.91) 0.87
One day later 45±5 45±5 0 (−2.24 to 2.24) 0.79
PEF (L/min)
Pre-intervention 475±67 482±69 −7 (−37.50 to 23.50) 0.69
Post-intervention 333±59 356±55 −23 (−48.67 to 2.67) 0.67
One day later 342±55 360±59 −18 (−43.55 to 7.55) 0.56
Abbreviations: VC: Vital capacity; PEF: Peak expiratory flow; NIV: Non-invasive ventilation.
of significance in arterial oxygen pressure, alveolar recruitment 5. Conclusion
resulted in a reduced need for supplemental oxygen, which was
reflected in the improved effectiveness of gas exchange. The use of NIV immediately after extubation for patients
Therefore, it was possible to maintain the oxygenation levels undergoing CABG demonstrated significantly positive impacts,
of patients for a longer duration with a lower O supply, thereby such as reducing the loss of functional capacity, decreasing the
rate of reintubation, and improving blood gas exchange, F O ,
2
decreasing the toxicity associated with oxygen use. In line with and the PaO /F O ratio. I 2
our results, Landoni et al. [17] demonstrated that NIV is a useful 2 I 2
tool to decrease respiratory work, reduce atelectasis, prevent Acknowledgments
respiratory failure, and improve gas exchange.
According to Laizo et al. [27], complications related to None.
respiratory function are the main causes of increased length of Funding
hospital stay. Since the rate of respiratory complications was
low in our study, particularly in the NIVI group, this may justify None.
the reduction in the length of hospital stay. This decrease can Conflicts of Interest
contribute to lower hospital costs and as a preventive factor for
future complications associated with prolonged hospital stay, The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
such as infections and loss of muscle mass. Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Systematic reviews found that immediate NIV did not achieve
a significant result in terms of length of stay in the ICU or The study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee
hospital [17,28]. This can be justified by the patient profiles studied, of Noble College in Feira de Santana, Brazil (approval number:
who had low ejection fractions, hypoactivity, and important deficits 1,405,821). All patients were informed about the study’s
in muscle strength associated with heart failure. Contrary to our objectives and provided written informed consent.
study, the patients evaluated did not present any hemodynamic Consent for Publication
instability before NIV, did not need surgical reintervention, and
mainly obtained positive results on the functionality scale. All research participants authorized the release of their data
In the literature and clinical practice, the choice of whether through a written and signed document.
to perform NIV on the first day after surgery or immediately Availability of Data
after extubation remains controversial. This work is evidence
that NIV immediately after extubation generates better clinical Data are available from the corresponding author on
and functional results a few hours after surgery. Therefore, reasonable request.
performing NIV immediately after extubation in selected
patients should be adopted as a routine practice. References
One of the limitations of this study is the lack of sample size [1] Daltro FMS, De Seixas Rocha M, Oliveira L. Effectiveness
calculation, which would have helped reduce the error margin of positive expiratory pressure on the vital capacity of
and effectively strengthen the conclusion. Other limitations patients undergoing myocardial revascularization. Rev
include the absence of a pain assessment scale, such as the Visual Bras Fisioter. 2010;14(S1):450.
Analog Scale (VAS), which could have allowed patients to report [2] Lawton JS, Tamis-Holland JE, Bangalore S, Bates ER,
the degree of pain at the moment. In addition, the study did not Beckie TM, Bischoff JM, et al. 2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI
use a blind examiner for variables, such as blood gas analysis. guideline for coronary artery revascularization: Executive
Other limitations are the small sample size and the fact that the summary: A report of the American college of cardiology/
study was conducted at only one participating institution. American heart association joint committee on clinical
DOI: http://doi.org/10.36922/jctr.24.00011