Page 43 - JCTR-10-6
P. 43
Aminizadeh et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2024; 10(6): 348-356 353
has a protective effect on the mitochondrial genome in muscle
tissue post-exercise. In another study on human NP cells, they
showed that administration of MitoQ decreased apoptosis
and the expression of DRP1 and FIS1 while increasing the
expression of proteins involved in fusion [42]. In our study,
the administration of MitoQ neutralized the enhancing effects
of ET on fusion, and in addition, in the rats that performed
HIIT exercise, it enhanced fission by increasing the expression
of DRP1 protein (in the HIIT + MitoQ group). These findings
contradict the previous studies where MitoQ had no effect in
the groups that performed exercise [42]. Given that exercise,
particularly aerobic exercise influences the mitochondria and
MitoQ specifically targets the mitochondria, the results in the
ET + MitoQ and HIIT + MitoQ groups should align more
closely with predictions. Despite the contradiction with other
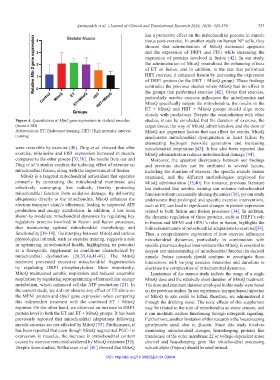
Figure 4. Quantitation of Mfn2 gene expression in skeletal muscles studies, it can be concluded that the duration of exercise, the
(mean ± SD) target tissue, the way of MitoQ administration, and the dose of
Abbreviation: ET: Endurance training; HIIT: High-intensity interval MitoQ are important factors that can affect the results. MitoQ
training ameliorates mitochondrial dysregulation in heart failure by
attenuating hydrogen peroxide generation and increasing
were reversible by exercise [40]. Ding et al. showed that after mitochondrial respiration [43]. It has also been reported that
exercise, mitofusins and FIS1 expression increased in muscle MitoQ administration reduces mitochondrial damage [44].
compared to the other groups [33,38]. The results from our and Moreover, the apparent discrepancy between our findings
Ding et al.’s studies confirm the inducing effect of exercise on and previous studies can be attributed to several factors,
mitochondrial fusion, along with the improvement of fission. including the duration of exercise, the specific muscle tissues
MitoQ is a targeted mitochondrial antioxidant that operates examined, and the different methodologies employed for
primarily by penetrating the mitochondrial membrane and MitoQ administration [35,40]. For instance, previous literature
selectively scavenging free radicals, thereby protecting has indicated that aerobic training can enhance mitochondrial
mitochondrial function from oxidative damage. By delivering function without necessarily altering dynamics [36], yet our study
ubiquinone directly to the mitochondria, MitoQ enhances the underscores that prolonged and specific exercise interventions,
electron transport chain’s efficiency, leading to improved ATP such as ET, can lead to significant changes in protein expression
production and energy metabolism. In addition, it has been related to both fusion and fission processes [34]. In addition,
shown to modulate mitochondrial dynamics by regulating key the dynamic regulation of these proteins, such as DRP1’s role
regulatory proteins involved in fission and fusion processes, in fission and MFN1 and OPA1’s roles in fusion, highlights the
thus maintaining optimal mitochondrial morphology and bidirectional nature of mitochondrial adaptations to exercise [38].
functionality [16-19]. The interplay between MitoQ and various Thus, a comprehensive exploration of how exercise influences
physiological stimuli, such as exercise training, suggests a role mitochondrial dynamics, particularly in combination with
in optimizing mitochondrial health, highlighting its potential specific pharmacological interventions like MitoQ, is essential to
as a therapeutic supplement in conditions characterized by deepen our understanding of mitochondrial function in skeletal
mitochondrial dysfunction [20,35,40,41-43]. The MitoQ muscle. Future research should continue to investigate these
treatment prevented excessive mitochondrial fragmentation interactions with varying exercise intensities and durations to
by regulating DRP1 phosphorylation. More importantly, elucidate the complexities of mitochondrial dynamics.
MitoQ maintained aerobic respiration and reduced anaerobic Limitations of the current study include the usage of a single
respiration by regulating reprogramming of intracellular energy MitoQ dose and the relatively short duration of MitoQ treatment.
metabolism, which enhanced cellular ATP production [21]. In The dose and treatment duration employed in this study were based
the current study, we did not observe any effect of ET alone on on the previous studies. In our experience, intraperitoneal injection
the MFN1 protein and Opa1 gene expression when comparing of MitoQ to rats could be lethal; therefore, we administered it
this independent treatment with the combined ET + MitoQ through the drinking water. The toxic effects of this supplement
regimen. On the other hand, we observed an increase in DRP1 may be related to the role of mitochondria as stress sensors, and
protein level in both the ET and ET + MitoQ groups. It has been it can modulate nuclear functioning through retrograde signaling.
previously reported that mitochondrial adaptations following Furthermore, another limitation of this research is the housekeeping
muscle exercise are not affected by MitoQ [35]. Furthermore, it gene/protein used, that is, β-actin. Since this study involves
has been reported that even though MitoQ augmented PGC-1α monitoring mitochondrial changes, housekeeping proteins like
expression in muscles, the increase in mitochondrial content translocase of the outer membrane 22 or voltage-dependent anion
caused by exercise remained unaltered by MitoQ treatment [35]. channel and housekeeping gene like mitochondrial processing
Despite these studies, Williamson et al. [41] showed that MitoQ subunit alpha (Pmpca) should be used instead.
DOI: http://doi.org/10.36922/jctr.24.00044