Page 10 - JCTR-11-2
P. 10
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research US-mediated drug delivery
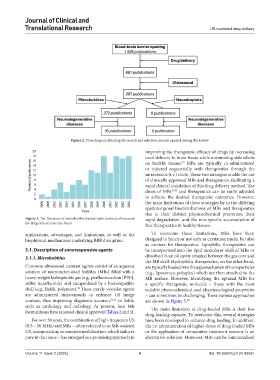
Figure 2. Flow diagram detailing the search and selection process applied during the review
improving the therapeutic efficacy of drugs by increasing
local delivery to brain tissue while minimizing side effects
on healthy tissues. MBs are typically co-administered
33
or injected sequentially with therapeutics through the
intravenous (i.v.) route. These two strategies enable the use
of clinically approved MBs and therapeutics, facilitating a
rapid clinical translation of this drug delivery method. The
doses of MBs 34,35 and therapeutics can be easily adjusted
to achieve the desired therapeutic outcomes. However,
the main limitations of these strategies lie in the differing
spatiotemporal biodistributions of MBs and therapeutics
due to their distinct physicochemical properties, their
Figure 3. The literature of microbubble/nanodroplet-assisted ultrasound rapid degradation, and the non-specific accumulation of
for drug delivery into the brain free therapeutics in healthy tissues.
applications, advantages, and limitations, as well as the To overcome these limitations, MBs have been
biophysical mechanisms underlying BBB disruption. designed to function not only as cavitation nuclei but also
as carriers for therapeutics. Lipophilic therapeutics can
3.1. Description of sonoresponsive agents be incorporated into the lipid monolayer shell of MBs or
3.1.1. Microbubbles dissolved in an oil cavity situated between the gas core and
the MB shell. Hydrophilic therapeutics, on the other hand,
Common ultrasound contrast agents consist of an aqueous are typically loaded into the aqueous lumen of nanoparticles
solution of micrometer-sized bubbles (MBs) filled with a (e.g., liposomes, polyplex) which are then attached to the
heavy-weight hydrophobic gas (e.g., perfluorocarbon [PFC], MB surface. However, identifying the optimal MBs for
sulfur hexafluoride) and encapsulated by a biocompatible a specific therapeutic molecule – those with the most
shell (e.g., lipids, polymers). These purely vascular agents suitable physicochemical and pharmacological properties
30
are administered intravenously to enhance US image – can sometimes be challenging. These various approaches
contrast, thus improving diagnostic accuracy 31,32 in fields, are shown in Figure 5. 28
such as cardiology and radiology. At present, four MB The main limitation of drug-loaded MBs is their low
formulations have received clinical approval (Tables 2 and 3).
drug-loading capacity. To overcome this, several strategies
For over 30 years, the combination of high-frequency US have been developed to enhance drug loading. In addition,
(0.5 – 10 MHz) and MBs – often referred to as MB-assisted the i.v. administration of higher doses of drug-loaded MBs
US, sonoporation, or sonopermeabilization, which induces or the application of consecutive treatment sessions is an
pore in the tissue – has emerged as a promising approach to alternative solution. Moreover, MBs can be functionalized
Volume 11 Issue 2 (2025) 4 doi: 10.36922/jctr.24.00061