Page 12 - JCTR-11-2
P. 12
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research US-mediated drug delivery
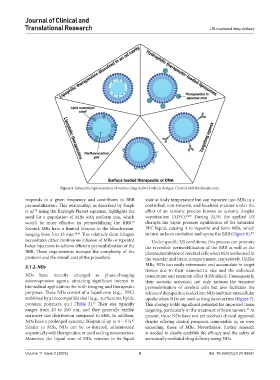
Figure 5. Schematic representation of various drug-delivery vehicle designs. Created with BioRender.com.
responds to a given frequency and contributes to BBB state at body temperature but can vaporize into MBs in a
permeabilization. This relationship, as described by Shapk controlled, non-invasive, and localized manner under the
et al. using the Rayleigh-Plesset equation, highlights the effect of an acoustic process known as acoustic droplet
38
need for a population of MBs with uniform size, which vaporization (ADV). 44,45 During ADV, the applied US
would be more effective in permeabilizing the BBB. disrupts the vapor pressure equilibrium of the saturated
39
Second, MBs have a limited lifespan in the bloodstream, PFC liquid, causing it to vaporize and form MBs, which
ranging from 5 to 15 min. 40,41 This relatively short lifespan in turn induces cavitation and opens the BBB (Figure 6). 46
necessitates either continuous infusion of MBs or repeated Under specific US conditions, this process can promote
bolus injections to achieve efficient permeabilization of the the reversible permeabilization of the BBB as well as the
BBB. These requirements increase the complexity of the plasma membrane of cerebral cells when NDs are located in
protocol and the overall cost of the procedure. the vascular and brain compartments, respectively. Unlike
3.1.2. NDs MBs, NDs can easily extravasate and accumulate in target
tissues due to their nanometric size and the enhanced
NDs have recently emerged as phase-changing penetration and retention effect (EPR effect). Consequently,
sonoresponsive agents, attracting significant interest in their acoustic activation not only induces the transient
biomedical applications for both imaging and therapeutic permeabilization of cerebral cells but also facilitates the
purposes. These NDs consist of a liquid core (e.g., PFC) release of therapeutics loaded into NDs and their intracellular
stabilized by a biocompatible shell (e.g., surfactants, lipids, uptake when NDs are used as drug nanocarriers (Figure 7).
proteins, polymers, etc.) (Table 3). Their size typically This strategy holds significant potential for improved tissue
42
ranges from 20 to 200 nm, and they generally exhibit targeting, particularly in the treatment of brain tumors. At
43
narrower size distribution compared to MBs. In addition, present, these NDs have not yet received clinical approval,
NDs have a prolonged systemic lifespan of up to 4 – 5 h. despite offering clinical prospects comparable to, or even
43
Similar to MBs, NDs can be co-injected, administered exceeding, those of MBs. Nevertheless, further research
sequentially with therapeutics, or used as drug nanocarriers. is needed to clearly establish the efficacy and the safety of
Moreover, the liquid core of NDs remains in its liquid acoustically mediated drug delivery using NDs.
Volume 11 Issue 2 (2025) 6 doi: 10.36922/jctr.24.00061