Page 99 - JCTR-11-3
P. 99
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research Household arsenic and bladder cancer
A B
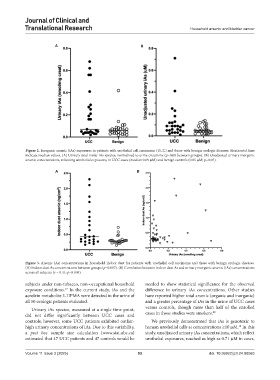
Figure 2. Inorganic arsenic (iAs) exposures in patients with urothelial cell carcinoma (UCC) and those with benign urologic diseases. Horizontal lines
indicate median values. (A) Urinary total molar iAs species, normalized to urine creatinine (p=0.08 between groups). (B) Unadjusted urinary inorganic
arsenic concentrations, reflecting urothelial exposures, in UCC cases (median 0.09 μM) and benign controls (0.05 μM; p=0.05).
A B
Figure 3. Arsenic (As) concentrations in household indoor dust for patients with urothelial cell carcinoma and those with benign urologic diseases.
(A) Indoor dust As concentrations between groups (p=0.007). (B) Correlation between indoor dust As and urinary inorganic arsenic (iAs) concentrations
across all subjects (r = 0.41; p=0.004).
subjects under non-tobacco, non-occupational household needed to show statistical significance for the observed
exposure conditions. In the current study, iAs and the difference in urinary iAs concentrations. Other studies
17
acrolein metabolite 3-HPMA were detected in the urine of have reported higher total arsenic (organic and inorganic)
all 50 urologic patients evaluated. and a greater percentage of iAs in the urine of UCC cases
Urinary iAs species, measured at a single time point, versus controls, though more than half of the enrolled
28
did not differ significantly between UCC cases and cases in those studies were smokers.
controls; however, some UCC patients exhibited outlier- We previously demonstrated that iAs is genotoxic to
high urinary concentrations of iAs. Due to this variability, human urothelial cells at concentrations ≥10 μM. In this
18
a post hoc sample size calculation (www.stat.ubc.ca) study, unadjusted urinary iAs concentrations, which reflect
estimated that 47 UCC patients and 47 controls would be urothelial exposures, reached as high as 0.71 μM in cases,
Volume 11 Issue 3 (2025) 93 doi: 10.36922/jctr.24.00065