Page 20 - JCTR-11-4
P. 20
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research Hidden cancer after VTE
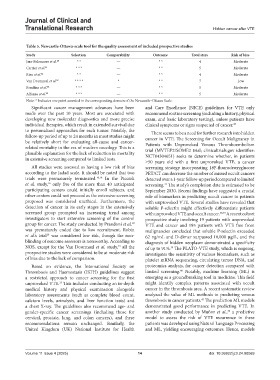
Table 5. Newcastle‑Ottawa‑scale tool for the quality assessment of included prospective studies
Study Selection Comparability Outcome Total stars Risk of bias
Jara-Palomares et al. 20 * * ― * * 4 Moderate
Carrier et al. 21 * * * ― * * 5 Moderate
Rieu et al. 22 * * ― * * 4 Moderate
Van Doormaal et al. 23 * * * * * * * 7 Low
Rondina et al. 24 * * * ― * * 5 Moderate
Alfonso et al. 25 * * * ― * * 5 Moderate
Note: * Indicates one point awarded in the corresponding domain of the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale.
Significant cancer management advances have been and Care Excellence (NICE) guidelines for VTE only
made over the past 10 years. Most are associated with recommend routine screening (including a history, physical
developing new molecular diagnostics and more precise exam, and basic laboratory testing), unless patients have
individual therapies, which result in extended survival due clinical symptoms or signs suspected of cancer. 36
to personalized approaches for each tumor. Notably, the There seems to be a need for further research into hidden
follow-up period of up to 24 months in most studies might cancer in VTE. The Screening for Occult Malignancy in
be relatively short for evaluating all-cause and cancer- Patients with Unprovoked Venous Thromboembolism
related mortality in the era of modern oncology. This is a trial (MVTEP2/SOME2 trial; clinicaltrials.gov identifier:
plausible explanation for the lack of reduction in mortality NCT04304651) seeks to determine whether, in patients
in extensive screening compared to limited tests.
≥50 years old with a first unprovoked VTE, a cancer
All studies were assessed as having a low risk of bias screening strategy incorporating 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose
according to the Jadad scale. It should be noted that two PET/CT can decrease the number of missed occult cancers
trials were prematurely terminated. 16,18 In the Piccioli detected over a 1-year follow-up period compared to limited
et al. study, only five of the more than 40 anticipated screening. The study’s completion date is estimated to be
16
37
participating centers could initially enroll subjects, and September 2030. Recent findings have suggested a crucial
other centers could not proceed as the extensive screening role of biomarkers in predicting occult cancer in patients
proposed was considered unethical. Furthermore, the with unprovoked VTE. Several studies have revealed that
detection of cancer in its early stages in the extensively soluble P-selectin might effectively differentiate patients
screened group prompted an increasing trend among with unprovoked VTE and occult cancer. 38,39 A recent cohort
investigators to start extensive screening of the control prospective study involving 19 patients with unprovoked
group for cancer. The study conducted by Prandoni et al. VTE and cancer and 195 patients with VTE free from
18
was prematurely ended due to low recruitment. Robin malignancies concluded that soluble P-selectin exceeded
et al.’s trial was considered low risk, though the non- 62 ng/mL and D-dimer surpassed 10,000 µg/L, and the
19
blinding of outcome assessors is noteworthy. According to diagnosis of hidden neoplasm demonstrated a specificity
NOS, except for the Van Doormaal et al. study, all the of up to 91%. The PLATO-VTE study, which is ongoing,
23
39
prospective studies were considered to be at moderate risk investigates the sensitivity of various biomarkers, such as
of bias due to the lack of comparison. platelet mRNA sequencing, circulating tumor DNA, and
Based on evidence, the International Society on proteomics analysis, for cancer detection compared with
40
Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH) guidelines suggest limited screening. Notably, machine learning (ML) is
a restricted approach to cancer screening for the first emerging as a groundbreaking tool in medicine. This field
unprovoked VTE. This includes conducting an in-depth might identify complex patterns associated with occult
35
medical history and physical examination alongside cancer in the thrombosis area. A recent systematic review
laboratory assessments (such as complete blood count, analyzed the value of ML methods in predicting venous
calcium levels, urinalysis, and liver function tests) and thrombosis in cancer patients. The prediction ML models
41
a chest X-ray. The guidelines also recommend age- and demonstrated good performance in predicting VTE. In
42
gender-specific cancer screenings (including those for another study conducted by Muñoz et al., a predictive
cervical, prostate, lung, and colon cancers), and these model to assess the risk of VTE recurrence in these
recommendations remain unchanged. Similarly, the patients was developed using Natural Language Processing
United Kingdom (UK) National Institute for Health and ML, yielding encouraging outcomes. Hence, models
Volume 11 Issue 4 (2025) 14 doi: 10.36922/jctr.24.00069