Page 17 - JCTR-9-4
P. 17
AboEl-Azm et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2023; 9(4): 222-235 233
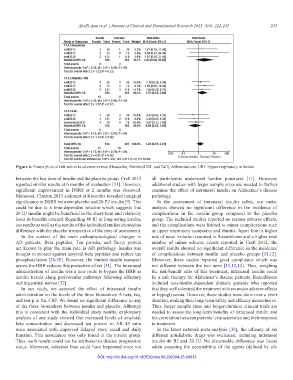
Figure 6. Forest plots of risk ration in adverse events (Headache, Rhinitis/URI, and Fall). Abbreviations: URI: Upper respiratory infection.
between the low dose of insulin and the placebo group. Craft 2012 all participants underwent lumbar punctures [11]. However,
reported similar results at 6 months of evaluation [11]. However, additional studies with larger sample sizes are needed to further
significant improvement in DSRS at 2 months was observed. examine the effect of intranasal insulin on Alzheimer’s disease
Moreover, Claxton 2013 endpoint at 4 months revealed marginal pathology.
significance in DSRS between placebo and 20 IU insulin [9]. This In the assessment of intranasal insulin safety, our meta-
could be due to a time-dependent relation which suggests that analysis showed no significant difference in the incidence of
20 IU insulin might be beneficial in the short-term and relatively complications in the insulin group compared to the placebo
loses its benefits onward. Regarding 40 IU or long-acting insulin, group. The included studies reported no serious adverse effects,
our results as well as the results of the individual studies showed no and the complications were limited to minor complications such
difference with the placebo irrespective of the time of assessment. as upper respiratory symptoms and rhinitis. Apart from a higher
In the context of the main pathophysiological changes in rate of nasal irritation reported in Rosenbloom and a higher total
AD patients, Beta peptides, Tau protein, and Tau-p protein number of minor adverse events reported in Craft 2012, the
are known to play the main role in AD pathology. Insulin was overall results showed no significant difference in the incidence
thought to protect against amyloid-beta peptides and reduce tau of complications between insulin and placebo groups [11,12].
phosphorylation [28-30]. However, the limited insulin transport Moreover, these studies reported good compliance which was
across the BBB reduces this protective effect [31]. The intranasal not different between the two arms [11,12,14]. Thus, weighing
administration of insulin was a new route to bypass the BBB as the risk-benefit ratio of this treatment, intranasal insulin could
insulin travels along perivascular pathways following olfactory be a safe therapy for Alzheimer’s disease patients. Rosenbloom
and trigeminal nerves [32]. included non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients who reported
In our study, we assessed the effect of intranasal insulin that they well tolerated the treatment with no major adverse effects
administration on the levels of the three biomarkers A beta, tau, or hypoglycemia. However, these studies were done over a short
and tau-p in the CSF. We found no significant difference in any duration, making their long-term safety and efficacy inconclusive.
of the three biomarkers between insulin and placebo. Although Thus, larger sample sizes and longer-duration clinical trials are
this is consistent with the individual study results, exploratory needed to assess the long-term benefits of intranasal insulin and
analysis of one study showed that increased levels of amyloid- the correlation between patients’ characteristics and their response
beta concentration and decreased tau protein–to–AB 42 ratio to treatment.
were associated with improved delayed story recall and daily In the latest network meta-analysis [33], the efficacy of six
function. This association was only found in the insulin group. different antidiabetic drugs was evaluated, including intranasal
Thus, such results could not be attributed to disease progression insulin 40 IU and 20 IU. No discernable difference was found
status. Moreover, selection bias could have happened since not when assessing the acceptability of the agents (defined by all-
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18053/jctres.09.202304.23-00013