Page 22 - JCTR-9-4
P. 22
238 Marchand et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2023; 9(4): 236-245
that resulted in a neonate who was born alive, and this ratio was We could not assess publication bias using the funnel plot
calculated to 100 embryo transfers. method, and Egger’s test is considered unreliable for less than ten
Two authors evaluated the methodological quality and the included studies [34,35].
risk of bias in included studies using the Cochrane risk of bias
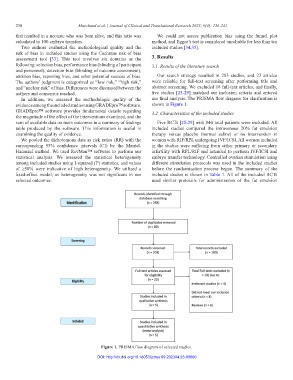
assessment tool [33]. This tool involves six domains as the 3. Results
following: selection bias, performance bias (blinding of participant 3.1. Results of the literature search
and personnel), detection bias (blinding of outcome assessment),
attrition bias, reporting bias, and other potential sources of bias. Our search strategy resulted in 283 studies, and 23 articles
The authors’ judgment is categorized as “low risk,” “high risk,” were reliable for full-text screening after performing title and
and “unclear risk” of bias. Differences were discussed between the abstract screening. We excluded 18 full-text articles, and finally,
authors and consensus reached. five studies [25-29] matched our inclusion criteria and entered
In addition, we assessed the methodologic quality of the our final analysis. The PRISMA flow diagram for clarification is
evidence among the included studies using GRADEpro™ software. shown in Figure 1.
GRADEpro™ software provides fundamental details regarding 3.2. Characteristics of the included studies
the magnitude of the effect of the interventions examined, and the
sum of available data on main outcomes in a summary of findings Five RCTs [25-29] with 840 total patients were included. All
table produced by the software. This information is useful in included studies compared the intravenous 20% fat emulsion
examining the quality of evidence. therapy versus placebo (normal saline) or no intervention in
We pooled the dichotomous data as risk ratios (RR) with the women with RIF/RPL undergoing IVF/ICSI. All women included
corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI) by the Mantel- in the studies were suffering from either primary or secondary
Haenszel method. We used RevMan™ software to perform our infertility with RPL/RIF and intended to perform IVF/ICSI and
statistical analysis. We assessed the statistical heterogeneity embryo transfer technology. Controlled ovarian stimulation using
among included studies using I-squared (I ) statistics, and values different stimulation protocols was used in the included studies
2
of ≥50% were indicative of high heterogeneity. We utilized a before the randomization process began. The summary of the
fixed-effect model, as heterogeneity was not significant in our included studies is shown in Table 1. All of the included RCTs
selected outcomes. used similar protocols for administration of the fat emulsion
Figure 1. PRISMA flow diagram of selected studies.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18053/jctres.09.202304.23-00060