Page 24 - JCTR-9-6
P. 24
388 Miyake et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2023; 9(6): 381-391
A
B
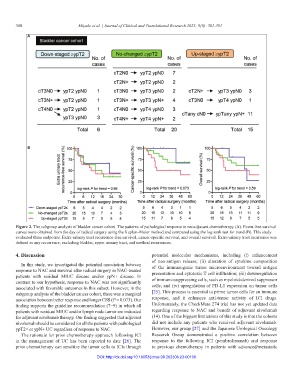
Figure 2. The subgroup analysis of bladder cancer cohort. The patterns of pathological response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (A). Event-free survival
curves were obtained from the day of radical surgery using the Kaplan–Meier method and compared using the log-rank test for trend (B). This study
evaluated three endpoints: Extra-urinary tract recurrence-free survival, cancer-specific survival, and overall survival. Extra-urinary tract recurrence was
defined as any recurrence, excluding bladder, upper urinary tract, and urethral recurrences.
4. Discussion potential molecular mechanisms, including (i) enhancement
of neo-antigen release; (ii) alteration of cytokine composition
In this study, we investigated the potential association between of the immunogenic tumor microenvironment toward antigen
response to NAC and survival after radical surgery in NAC-treated presentation and cytotoxic T cell infiltration; (iii) downregulation
patients with residual MIUC disease and/or ypN+ disease. In
contrast to our hypothesis, response to NAC was not significantly of immune-suppressing cells, such as myeloid-derived suppressor
associated with favorable outcomes in this subset. However, in the cells; and (iv) upregulation of PD-L1 expression on tumor cells
subgroup analysis of the bladder cancer cohort, there was a marginal [25]. This process is essential to prime tumor cells for an immune
association between better response and longer CSS (P = 0.073). Our response, and it enhances anti-tumor activity of ICI drugs.
finding supports the guideline recommendation (7−9) in which all Unfortunately, the CheckMate 274 trial has not yet updated data
patients with residual MIUC and/or lymph node tumor are indicated regarding response to NAC and benefit of adjuvant nivolumab
for adjuvant nivolumab therapy. Our finding suggested that adjuvant (14). One of the biggest limitations of this study is that the cohorts
nivolumab should be considered for all the patients with pathological did not include any patients who received adjuvant nivolumab.
ypT2≤ or ypN+ UC regardless of response to NAC. However, our group [27] and the Japanese Urological Oncology
The rationale for prior chemotherapy approach following ICI Research Group demonstrated a positive correlation between
in the management of UC has been reported to date [26]. The response to the following ICI (pembrolizumab) and response
prior chemotherapy can sensitize the tumor cells to ICIs through to previous chemotherapy in patients with advanced/metastatic
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18053/jctres.09.202306.23-00106