Page 25 - JCTR-9-6
P. 25
Miyake et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2023; 9(6): 381-391 389
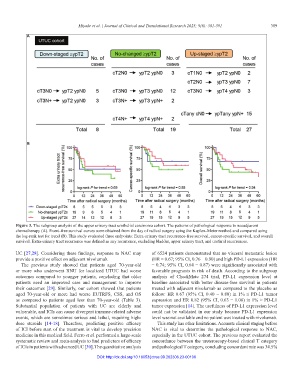
A
B
Figure 3. The subgroup analysis of the upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma cohort. The patterns of pathological response to neoadjuvant
chemotherapy (A). Event-free survival curves were obtained from the day of radical surgery using the Kaplan–Meier method and compared using
the log-rank test for trend (B). This study evaluated three endpoints: Extra-urinary tract recurrence-free survival, cancer-specific survival, and overall
survival. Extra-urinary tract recurrence was defined as any recurrence, excluding bladder, upper urinary tract, and urethral recurrences.
UC [27,28]. Considering these findings, response to NAC may of 6524 patients demonstrated that no visceral metastatic lesion
provide a positive effect on adjuvant nivolumab. (HR = 0.67; 95% CI, 0.76 − 0.90) and high PD-L1 expression (HR
The previous study showed that patients aged 70-year-old = 0.74; 95% CI, 0.64 − 0.87) were significantly associated with
or more who underwent RNU for localized UTUC had worse favorable prognosis in risk of death. According to the subgroup
outcomes compared to younger patients, concluding that older analysis of CheckMate 274 trial, PD-L1 expression level at
patients need an improved care and management to improve baseline associated with better disease-free survival in patients
their outcomes [29]. Similarly, our cohort showed that patients treated with adjuvant nivolumab as compared to the placebo as
aged 70-year-old or more had worse EUTRFS, CSS, and OS follow: HR 0.67 (95% CI, 0.40 − 0.80) in 1% ≤ PD-L1 tumor
as compared to patients aged less than 70-year-old (Table 3). expression and HR 0.82 (95% CI, 0.63 − 1.06) in 1% > PD-L1
Substantial population of patients with UC are elderly and tumor expression [14]. The usefulness of PD-L1 expression level
vulnerable, and ICIs can cause divergent immune-related adverse could not be validated in our study because PD-L1 expression
events, which are sometimes serious and lethal, requiring high- level was not available and no patient was treated with nivolumab.
dose steroids [14-18]. Therefore, predicting positive efficacy This study has other limitations. Accurate clinical staging before
of ICI before start of the treatment is vital to develop precision NAC is vital to determine the pathological response to NAC,
medicine in this medical field. Ferro et al. performed a large-scale especially in the UTUC cohort. The previous report evaluated the
systematic review and meta-analysis to find predictors of efficacy concordance between the ureteroscopy-based clinical T category
of ICIs in patients with advanced UC [30]. The quantitative analysis and pathological T category, concluding concordant rate was 34.5%
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18053/jctres.09.202306.23-00106