Page 102 - MI-1-2
P. 102
Microbes & Immunity Klebsiella pneumoniae diagnosed by NGS
A B C D
E F G H
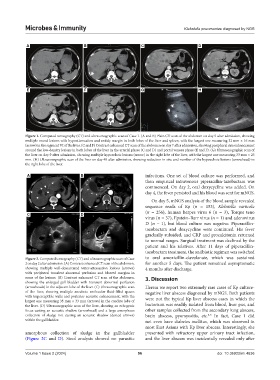
Figure 1. Computed tomography (CT) and ultrasonographic scan of Case 1. (A and B) Plain CT scan of the abdomen on day 5 after admission, showing
multiple round lesions with hypoattenuation and untidy margin in both lobes of the liver and spleen, with the largest one measuring 32 mm × 16 mm
(arrow) in the segment VI of the liver. (C and F) Contrast enhanced CT scan of the abdomen on day 7 after admission, showing peripheral rim enhancement
around the low-density lesions in both lobes of the liver in the arterial phase (C and D) and portal venous phase (E and F). (G) Ultrasonographic scan of
the liver on day 9 after admission, showing multiple hypoechoic lesions (arrow) in the right lobe of the liver, with the largest one measuring 33 mm × 25
mm. (H) Ultrasonographic scan of the liver on day 48 after admission, showing reduction in size and number of the hypoechoic lesions (arrowhead) in
the right lobe of the liver.
A B infections. One set of blood culture was performed, and
then empirical intravenous piperacillin-tazobactam was
commenced. On day 2, oral doxycycline was added. On
day 4, the fever persisted and his blood was sent for mNGS.
On day 5, mNGS analysis of the blood sample revealed
sequence reads of Kp (n = 153), Klebsiella variicola
(n = 256), human herpes virus 6 (n = 3), Torque teno
C D
virus (n = 37), Epstein–Barr virus (n = 1) and adenovirus
D (n = 1), but blood culture was negative. Piperacillin-
tazobactam and doxycycline were continued. His fever
gradually subsided, and CRP and procalcitonin returned
to normal ranges. Surgical treatment was declined by the
patient and his relatives. After 11 days of piperacillin-
tazobactam treatment, the antibiotic regimen was switched
Figure 2. Computed tomography (CT) and ultrasonographic scan of Case to oral amoxicillin-clavulanate, which was sustained
2 on day 2 after admission. (A) Contrast enhanced CT scan of the abdomen, for another 5 days. The patient remained asymptomatic
showing multiple well-demarcated water-attenuation lesions (arrows) 4 months after discharge.
with peripheral transient abnormal perfusion and blurred margins in
some of the lesions. (B) Contrast enhanced CT scan of the abdomen, 3. Discussion
showing the enlarged gall bladder with transient abnormal perfusion
(arrowheads) in the adjacent lobe of the liver. (C) Ultrasonographic scan Herein we report two extremely rare cases of Kp culture-
of the liver, showing multiple anechoic unilocular fluid-filled spaces negative liver abscess diagnosed by mNGS. Both patients
with imperceptible walls and posterior acoustic enhancement, with the were not the typical Kp liver abscess cases in which the
largest one measuring 35 mm × 33 mm (arrows) in the caudate lobe of
the liver. (D) Ultrasonographic scan of the liver, showing an echogenic bacterium was readily isolated from blood, liver pus, and
focus casting an acoustic shadow (arrowhead) and a large amorphous other samples collected from the secondary lung abscess,
collection of sludge not casting an acoustic shadow (dotted arrows) brain abscess, pyomyositis, etc. In fact, Case 1 did
3-5
within the gallbladder. not even have diabetes mellitus, which was observed in
most East Asians with Kp liver abscess. Interestingly, she
amorphous collection of sludge in the gallbladder presented with refractory upper urinary tract infection,
(Figure 2C and D). Stool analysis showed no parasitic and the liver abscess was incidentally revealed only after
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 96 doi: 10.36922/mi.4636