Page 107 - MI-1-2
P. 107
Microbes & Immunity Cedecea lapagei in a case of pleural empyema
due to a road accident, and offer a literature review of the
Cedecea cases documented.
2. Case presentation
A 60 year old female patient was referred to the emergency
department with a history of breathing difficulty along
with pain on her right side of chest since one day. She met
with a road traffic accident one week before. She had been
to the private hospital for management of her conditions.
A computed tomography (CT) of the chest revealed
comminuted fracture of the right scapula, fracture third
to eighth rib, and moderate right hemothorax that caused
right-side lung collapse. Head CT showed temporal bone
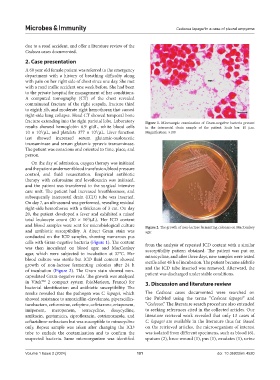
fracture extending into the right parietal lobe. Laboratory Figure 1. Microscopic examination of Gram-negative bacteria present
results showed hemoglobin 6.9 g/dL, white blood cells in the intercostal drain sample of the patient. Scale bar: 10 µm.
10 × 10 /µL, and platelets 377 × 10 /µL. Liver function Magnification: ×100
3
3
test showed increased serum glutamic-oxaloacetic
transaminase and serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase.
The patient was conscious and oriented to time, place, and
person.
On the day of admission, oxygen therapy was initiated
and the patient underwent blood transfusion, blood pressure
control, and fluid resuscitation. Empirical antibiotic
therapy with cefuroxime and levofloxacin was initiated,
and the patient was transferred to the surgical intensive
care unit. The patient had increased breathlessness, and
subsequently intercostal drain (ICD) tube was inserted.
On day 7, an ultrasound was performed, revealing residual
right-side hemothorax with a thickness of 3 cm. On day
20, the patient developed a fever and exhibited a raised
total leukocyte count (20 × 10 /µL). Her ICD content
3
and blood samples were sent for microbiological culture Figure 2. The growth of non-lactose fermenting colonies on MacConkey
and antibiotic susceptibility. A direct Gram stain was agar
conducted on the ICD samples, showing numerous pus
cells with Gram-negative bacteria (Figure 1). The content from the analysis of repeated ICD content with a similar
was then inoculated on blood agar and MacConkey susceptibility pattern obtained. The patient was put on
agar, which were subjected to incubation at 37°C. Her minocycline, and after three days, new samples were tested
blood culture was sterile but ICD fluid content showed
growth of non-lactose fermenting colonies after 24 h sterile after 48 h of incubation. The patient became afebrile
of incubation (Figure 2). The Gram stain showed non- and the ICD tube inserted was removed. Afterward, the
capsulated Gram-negative rods. The growth was analyzed patient was discharged under stable conditions.
in Vitek 2 compact system (bioMerieux, France) for 3. Discussion and literature review
bacterial identification and antibiotic susceptibility. The
results revealed that the pathogen was C. lapagei, which The Cedecea cases documented were searched on
showed resistance to amoxicillin-clavulanate, piperacillin- the PubMed using the terms “Cedecea lapagei” and
tazobactam, cefuroxime, cefepime, ceftriaxone, ertapenem, “Cedecea.” The literature search procedure also extended
imipenem, meropenem, tetracycline, doxycycline, to seeking references cited in the collected articles. Our
amikacin, gentamicin, ciprofloxacin, cotrimoxazole, and literature retrieval work revealed that only 13 cases of
ceftazidime-avibactam but was susceptible to minocycline C. lapagei are available in the literature thus far. Based
only. Repeat sample was taken after changing the ICD on the retrieved articles, the microorganism of interest
tube to exclude the contamination and to confirm the was isolated from different specimens, such as blood (6),
suspected bacteria. Same microorganism was identified sputum (2), knee wound (1), pus (1), exudates (1), urine
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 101 doi: 10.36922/mi.4520