Page 21 - MI-1-2
P. 21
Microbes & Immunity Homologous versus heterologous COVID-19 vaccines
Figure 1. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta chart demonstrating the details of screening and selecting articles
A
Figure 3. Overview of the different vaccination strategies used for the first
B and second doses of the COVID-19 vaccination
was 9.2, which suggests there was no significant difference
in the protection conferred by the heterologous vaccination
regime compared to the homologous vaccination regime.
22
A margin of GMR >0.63 was used to determine the non-
inferiority of the heterologous group. On the other hand,
22
participants who received heterologous BNT/ChAd had
lower spike IgG antibody levels compared to participants
vaccinated with homologous BNT/BNT (7,133 EU/mL
to 14,080 EU/mL) with a GMR of 0.51. It is important
22
to highlight that when a comparison was made between
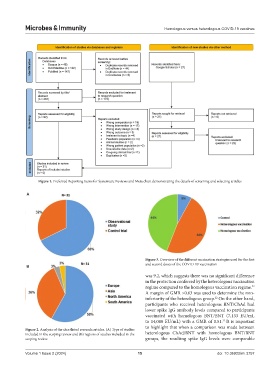
Figure 2. Analysis of the shortlisted research articles. (A) Type of studies
included in the scoping review and (B) regions of studies included in the heterologous ChAd/BNT with homologous BNT/BNT
scoping review groups, the resulting spike IgG levels were comparable
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 15 doi: 10.36922/mi.3757