Page 15 - MI-2-3
P. 15
Microbes & Immunity PTMs in Sepsis: Mechanisms and therapy
Sirtuins (SIRTs), a family of nicotinamide adenine degradation by recruiting E3 ligase MARCH7, reducing
dinucleotide (NAD)-dependent deacetylases (SIRT1-7), NLRP3 ubiquitination but increasing its acetylation,
exhibit antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, and anti-inflammatory thereby exacerbating macrophage pyroptosis, and
properties, positioning them as key regulators in sepsis. systemic inflammatory injury. SIRT3, localized in the
94
99
Specifically, SIRT1 activation, mediated by growth mitochondrial matrix, mitigates oxidative stress and
100
arrest-specific transcript 5 (GAS5), nicaraven (AVS), inflammation in sepsis-induced ALI by inhibiting p53
and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), attenuates acetylation, an effect enhanced by menadione 4 (MK-4).
101
inflammation by inhibiting high mobility group box SIRT7 (the only sirtuin located in the nucleolus) is required
1 (HMGB1) and NF-κB p65 acetylation, respectively, for ribosomal DNA transcription. SIRT7 inactivation
100
thereby improving survival and mitigating organ damage by Zn increases parkin acetylation, promoting parkin-
2+
in sepsis models. 95-97 NMN also inhibits NF-κB p65 mediated mitophagy and inhibiting NLRP3 activation,
phosphorylation, thereby preventing sepsis-induced ALI. 97 thus ameliorating AKI in sepsis. 102
SIRT2 is a negative regulatory factor of autophagy. SIRTs and acetylation critically regulate inflammation
Its inhibition promotes autophagy and attenuates and sepsis progression, making them promising
septic AKI through increasing FOXO1 acetylation. therapeutic targets. Molecules such as GAS5, AVS, NMN,
98
Furthermore, the costimulatory molecule glucocorticoid- GITR, MK-4, and Zn may offer avenues for targeted
2+
induced TNFR-related protein (GITR) induces SIRT2 intervention.
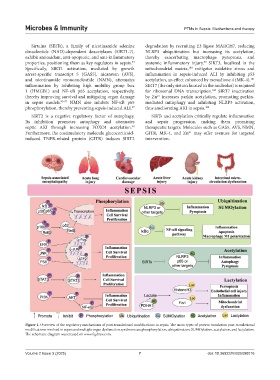
Figure 1. Overview of the regulatory mechanisms of post-translational modifications in sepsis. The main types of protein translation post-translational
modifications involved in sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome are phosphorylation, ubiquitination, SUMOylation, acetylation, and lactylation.
The schematic diagram was created on www.figdraw.com.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 7 doi: 10.36922/MI025090016