Page 11 - MSAM-1-3
P. 11
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Biodegradable sustainable electronics
A B
C
D
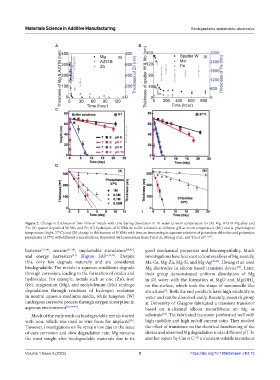
Figure 2. Change in thickness of thin films of metals with time during dissolution in DI water at room temperature for (A) Mg, AZ31B Mg alloy and
Zn; (B) sputter deposited W, Mo, and Fe; (C) hydrolysis of Si NMs in buffer solutions at different pH at room temperature (left) and at physiological
temperature (right, 37°C); and (D) change in thicknesses of Si NMs with time on immersing in aqueous solutions of potassium chlorides and potassium
phosphates at 37°C with different concentrations. Reprinted with permission from Yin et al., Hwang et al., and Yin et al .[3,13,14] .
batteries [33,34] , sensors [35-38] , implantable stimulators [39,40] , good mechanical properties and biocompatibility. Much
and energy harvesters (Figure 3A) [6,42,43] . Despite investigations have been carried out on alloys of Mg, namely,
[41]
this, only few degrade naturally and are considered Ma-Ca, Mg-Zn, Mg-Si, and Mg-Ag [22,29] . Hwang et al. used
biodegradable. The metals in aqueous conditions degrade Mg electrodes in silicon-based transient device . Later,
[17]
through corrosion, leading to the formation of oxides and their group demonstrated uniform dissolution of Mg
hydroxides. For example, metals such as zinc (Zn), iron in DI water with the formation of MgO and Mg(OH)
2
(Fe), magnesium (Mg), and molybdenum (Mo) undergo on the surface, which took the shape of nanoneedle-like
degradation through reactions of hydrogen evolution structures . Both the end products have high solubility in
[3]
in neutral aqueous mediums media, while tungsten (W) water and can be dissolved easily. Recently, research group
undergoes corrosive process through oxygen absorption in at University of Glasgow fabricated a transient transistor
aqueous environment [23,44-49] . based on n-channel silicon nanoribbons on Mg as
[24]
Much of the early work on biodegradable metals started substrate . The fabricated transistor performed well with
with iron, which was used in wire form for implants . high mobility and high on/off current ratio. They studied
[50]
However, investigations on Fe remain low due to the issue the effect of transience on the electrical functioning of the
of easy corrosion and slow degradation rate. Mg remains device and observed Mg degradation under different pH. In
the most sought after biodegradable materials due to its another report by Cao et l., a transient volatile memristor
[51]
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2022) 5 https://doi.org/10.18063/msam.v1i3.15