Page 59 - MSAM-1-4
P. 59
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing LPBF of Mg and its bio-applications
A B C
Figure 6. (A-C) BSE-SEM micrographs revealing the microstructure of the sample in the SLM-prepared WE43 with and without HIP treatment.
A D
B C
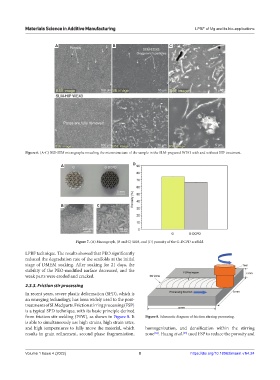
Figure 7. (A) Macrograph, (B and C) SEM, and (D) porosity of the G-DCPD scaffold.
LPBF technique. The results showed that PEO significantly
reduced the degradation rate of the scaffolds at the initial
stage of DMEM soaking. After soaking for 21 days, the
stability of the PEO-modified surface decreased, and the
weak parts were eroded and cracked.
2.3.3. Friction stir processing
In recent years, severe plastic deformation (SPD), which is
an emerging technology, has been widely used to the post-
treatments of SLMed parts. Friction stirring processing (FSP)
is a typical SPD technique, with its basic principle derived
from friction stir welding (FSW), as shown in Figure 8. It Figure 8. Schematic diagram of friction stirring processing.
is able to simultaneously use high strains, high strain rates,
and high temperatures to fully move the material, which homogenization, and densification within the stirring
[64]
[65]
results in grain refinement, second phase fragmentation, zone . Huang et al. used FSP to reduce the porosity and
Volume 1 Issue 4 (2022) 8 https://doi.org/10.18063/msam.v1i4.24